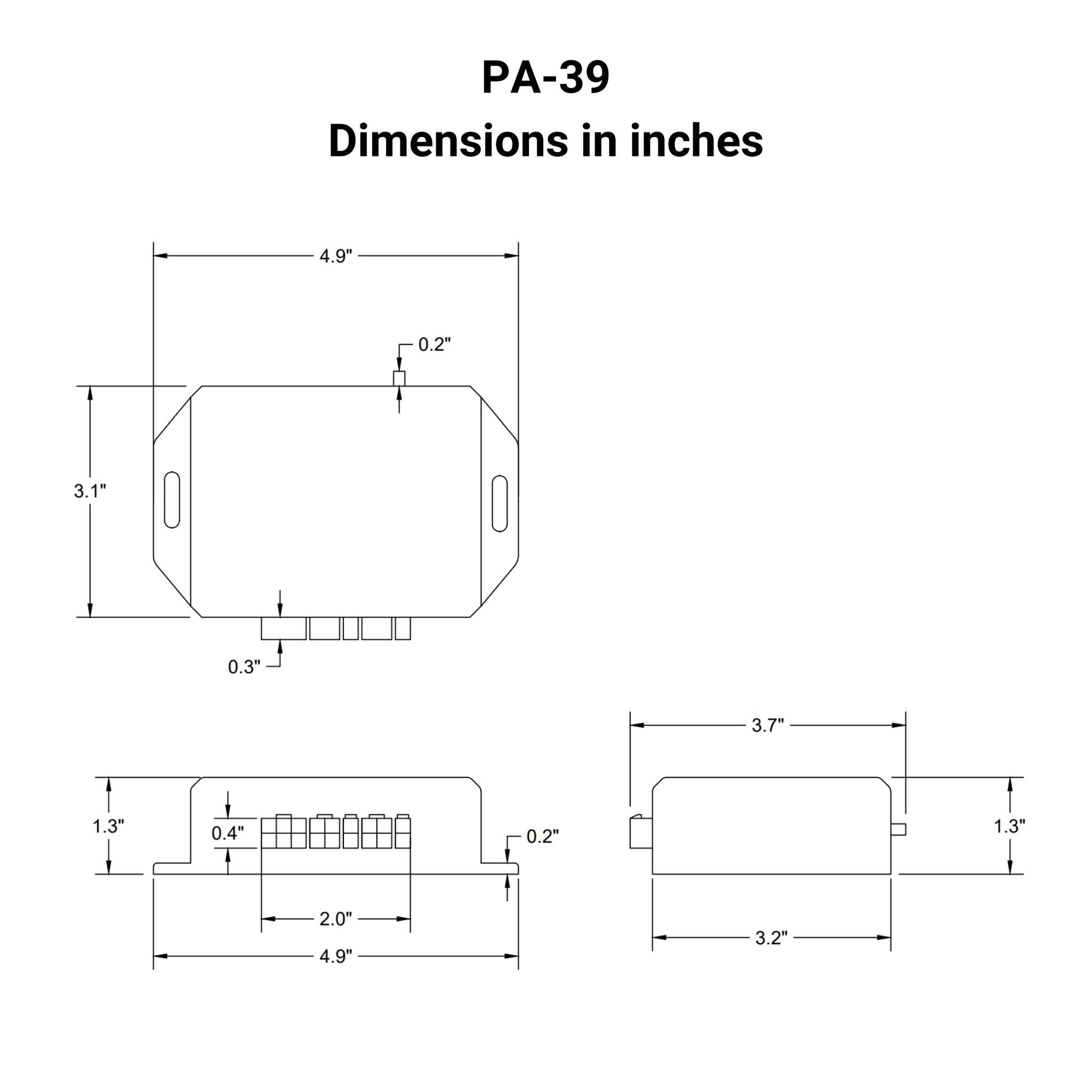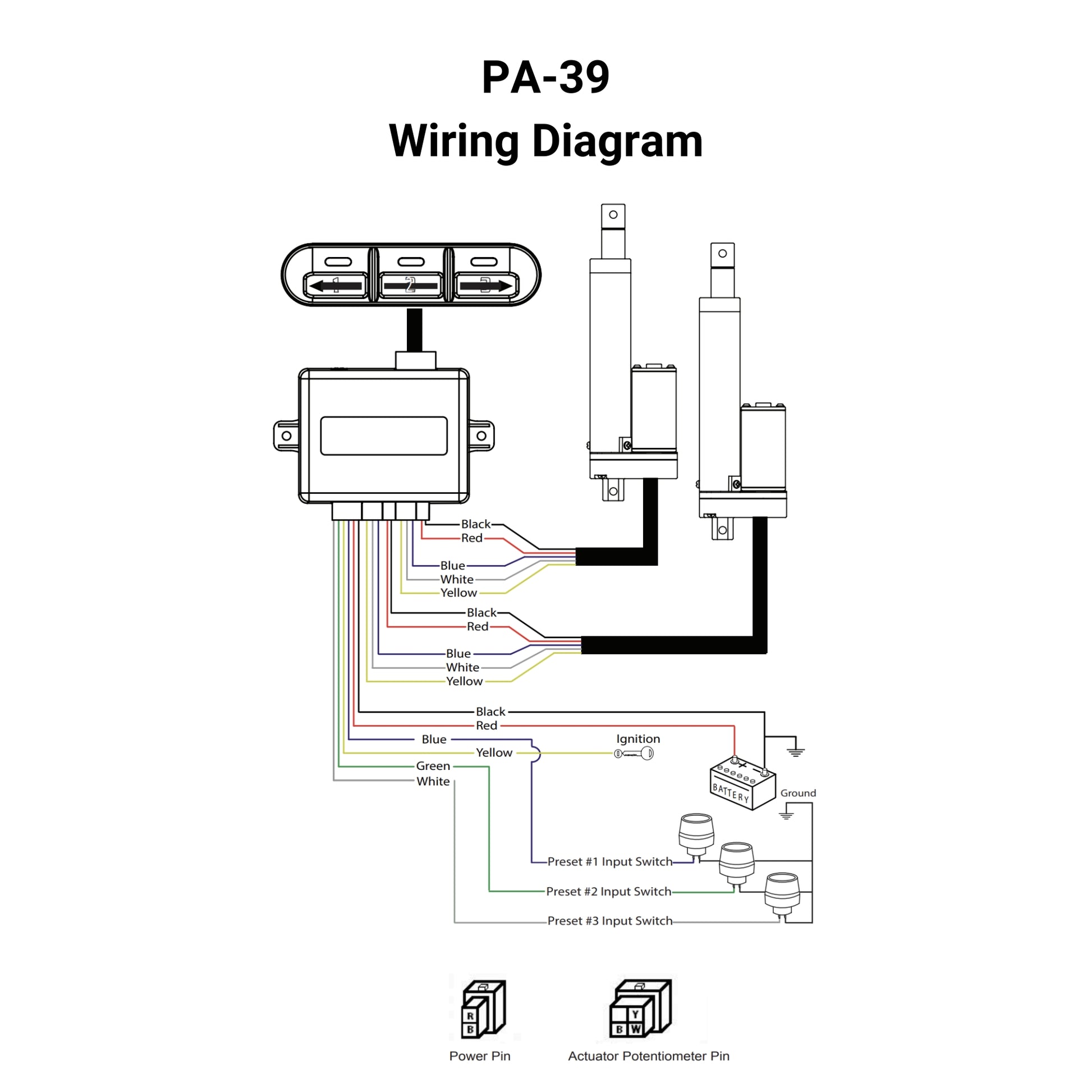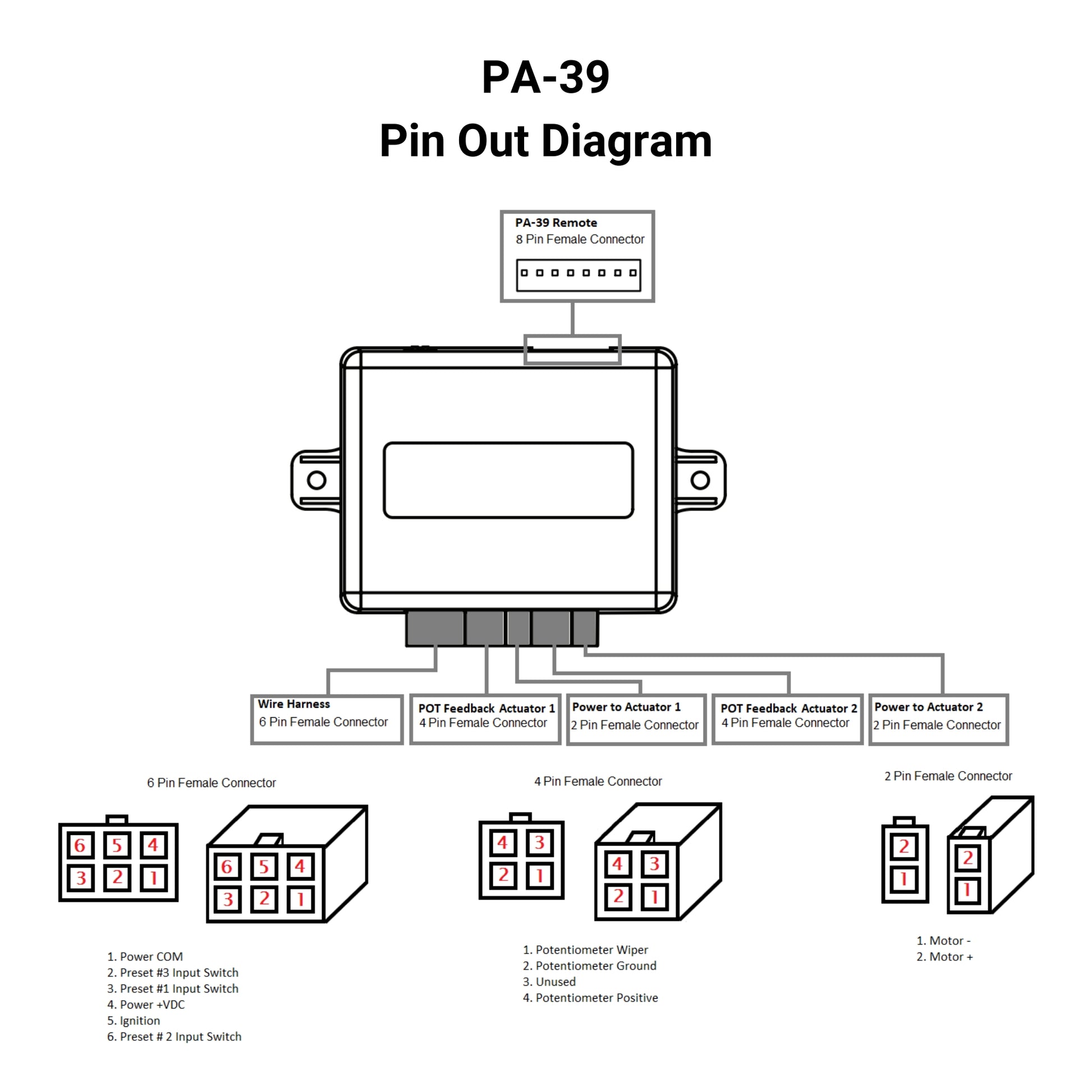
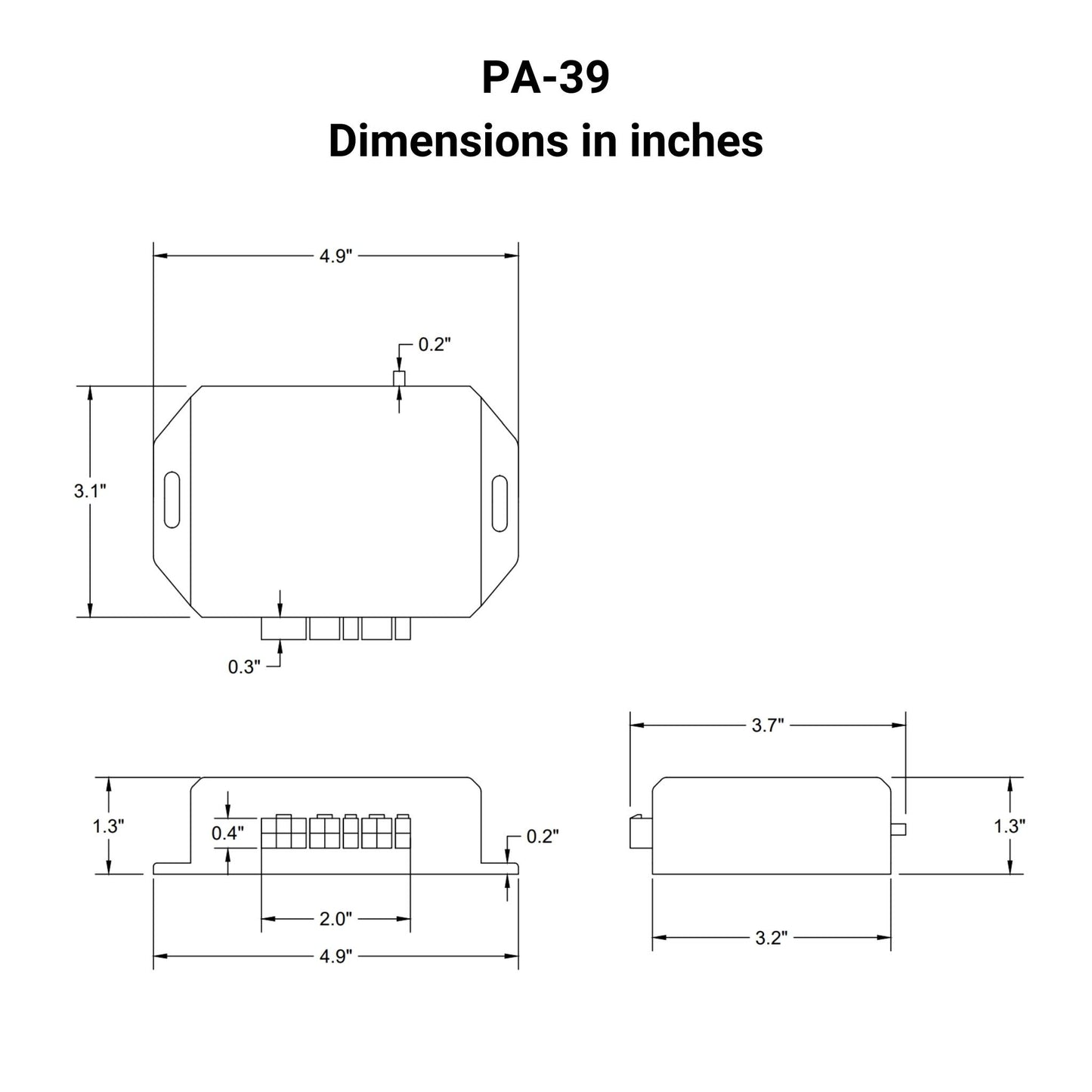
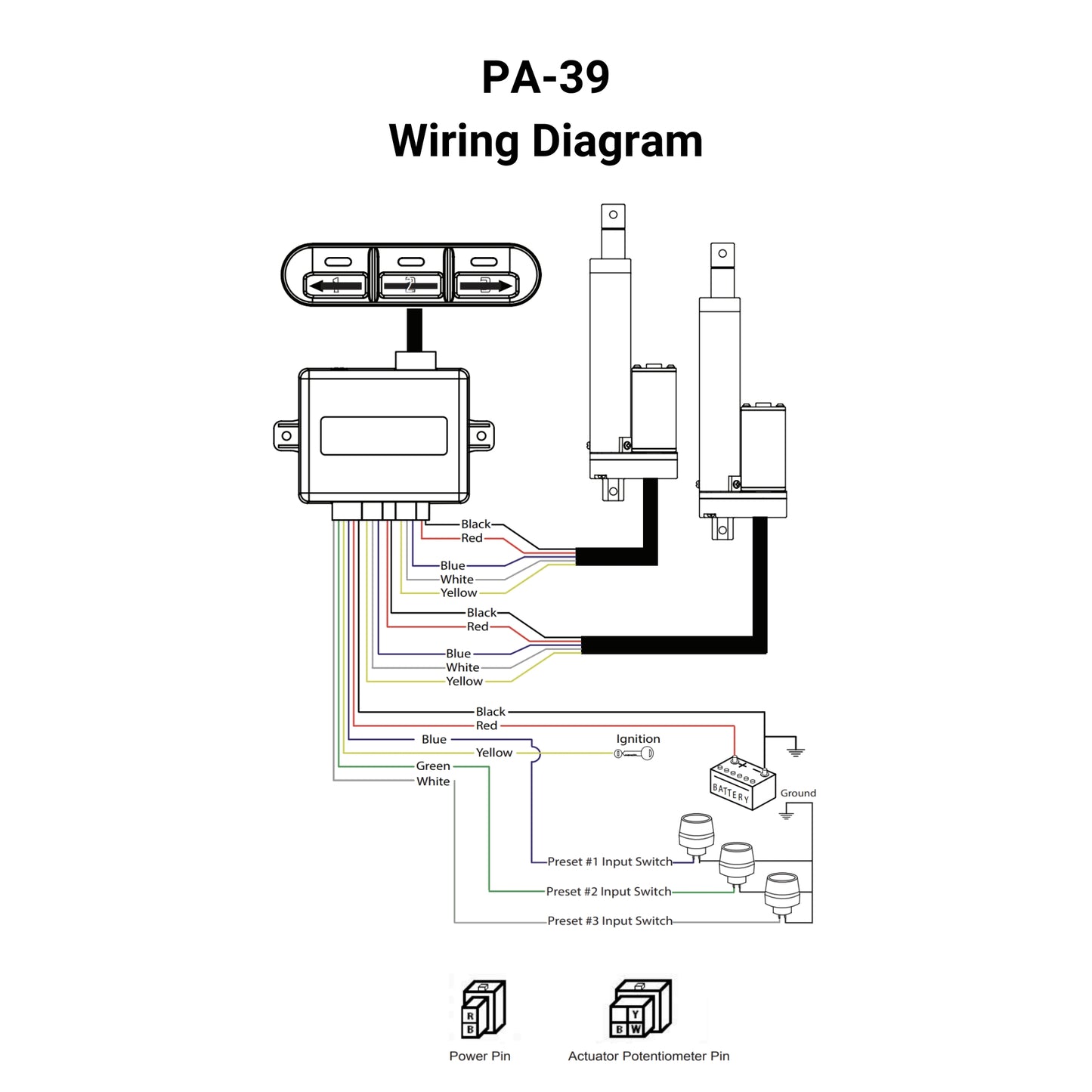
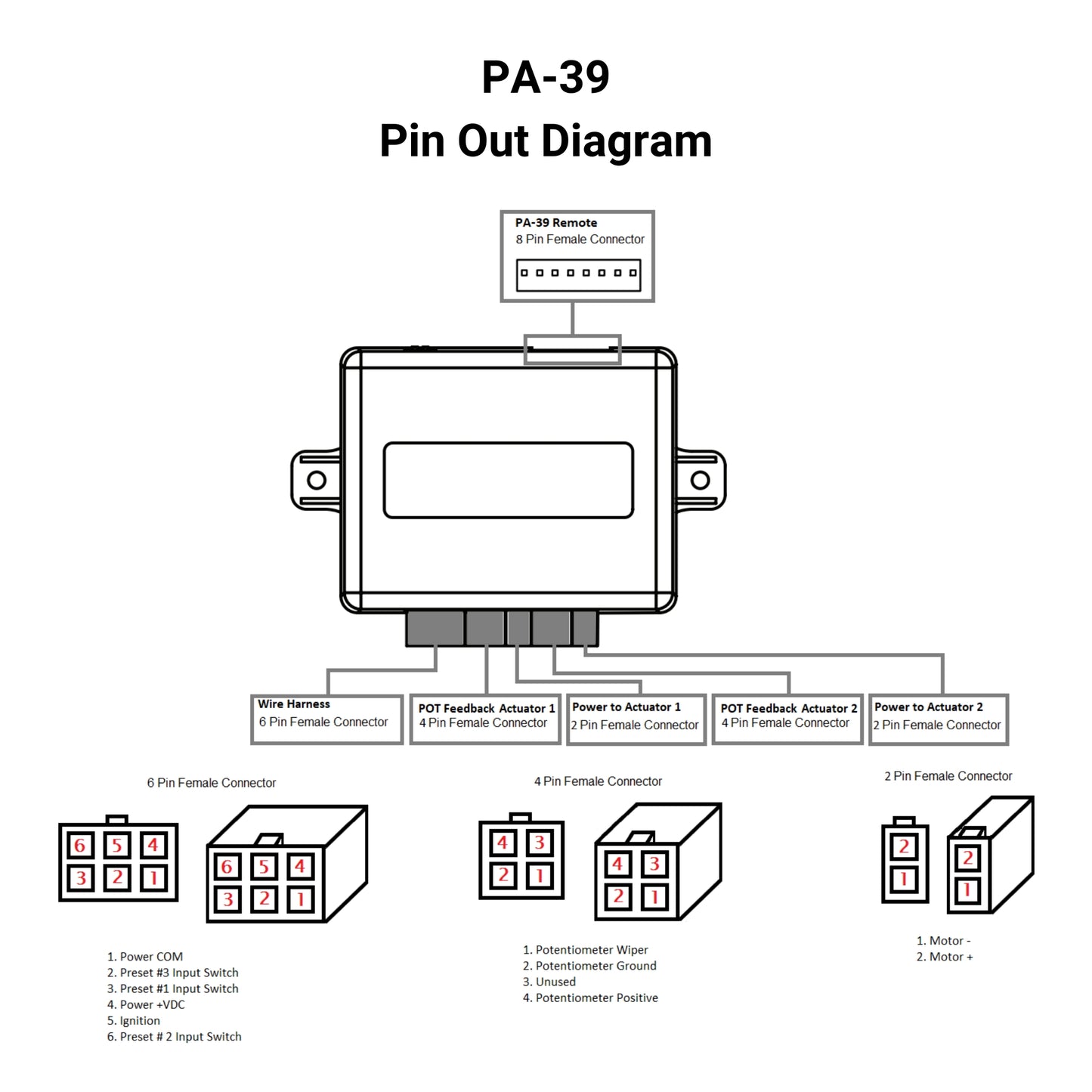
The PA-39 control box allows for individual or synchronous control of linear actuators with potentiometer feedback. The control box has the ability to save 3 preset locations, control linear actuators in sequential motion, and extend, stop, and retract movement.
*The PA-39 is the ideal 2-actuator control box if synchronization is essential to your application. It is important to ensure that the 12VDC power supply has a sufficient current rating to support all connected units. If you are in need of actuators to use with the PA-39, the PA-14P Feedback Linear Actuators are compatible with slight modification of the connectors.
For a more in-depth guide on the programming, please see the PA-39 User Manual.
* 30A (15A per channel) is possible provided you upgrade the supply wires to a thicker gauge. The fuse must be upgraded to 30A as well.
* Only compatible with potentiometer feedback actuators at 12 or 24 VDC. Controls 2 actuators with potentiometer feedback in sync or in sequence (one after the other). The PA-14P actuators are compatible with slight modifications to their connectors.
The PA-39 control box allows for individual or synchronous control of linear actuators with potentiometer feedback. The control box has the ability to save 3 preset locations, control linear actuators in sequential motion, and extend, stop, and retract movement.
*The PA-39 is the ideal 2-actuator control box if synchronization is essential to your application. It is important to ensure that the 12VDC power supply has a sufficient current rating to support all connected units. If you are in need of actuators to use with the PA-39, the PA-14P Feedback Linear Actuators are compatible with slight modification of the connectors.
For a more in-depth guide on the programming, please see the PA-39 User Manual.
* 30A (15A per channel) is possible provided you upgrade the supply wires to a thicker gauge. The fuse must be upgraded to 30A as well.
* Only compatible with potentiometer feedback actuators at 12 or 24 VDC. Controls 2 actuators with potentiometer feedback in sync or in sequence (one after the other). The PA-14P actuators are compatible with slight modifications to their connectors.
Following a set of standards is crucial for businesses to ensure their products and services can meet a level of quality that promotes customer satisfaction. At Progressive Automations, we aim for nothing but the best for our customers and strive toward continual improvements. Because of this, we are excited to announce that Progressive Automations is now ISO 9001:2015 certified!
Read MoreDepending on your application, there are different specification requirements you should consider when determining the linear actuator you need. These requirements include force, stroke, speed and mounting dimensions. For detailed actuator information, you can refer to either the datasheet or the specification table located on the selected actuator's product page. You can also contact us to speak with one of our expert engineers.
Duty cycle is the fraction of the working period in which a linear actuator can remain active. You can calculate the duty cycle of a linear actuator by using the following equation: Duty cycle (%) = (Time the linear actuator is active) / (Time for one working period)
For example: With a 25% duty cycle, an actuator can run for 5 minutes continuously before needing to rest for 15 minutes before operating.
Stroke is the travel distance of the extending rod. To find the stroke length you require, measure your application from the fully retracted position to the fully extended position. The difference will equal the stroke length you require.
We always recommend purchasing an actuator with a higher force rating than what the application requires. If unsure of your force requirements, this article may help you calculate this: How to Calculate Force to Find the Right Linear Actuator
Yes, this is possible. However, it does depend on the units you are currently using. To synchronize actuators, they require a form of feedback such as a potentiometer or hall effect sensors. For more information, see below some of our key content regarding linear actuator synchronization.
The control box you choose should be able to provide sufficient voltage and current rating to your actuator. If you are unsure of the specifications, please contact us.
Alternatively, you can also find compatible control boxes on your selected linear actuator's product page.
Backdriving is when an actuator starts sliding down under load, when it is either overloaded or when the actuator has been damaged. Watch the video.
What Does Dynamic and Static Load Ratings Mean?Dynamic load rating is the amount of weight an actuator can pull or push safely when being powered. Static load rating is the amount of weight the actuator can hold or withstand without back driving when it is not being powered. For example, let's just say you have an actuator installed on a window and the static load rating of the actuator is 100lbs, it could experience backdriving when there is a high wind event, which means there will be more pressure exerted on the actuator which would exceed the 100lbs load rating of the actuator.
What Is Lateral Loading?Lateral loading is when the actuator experiences forces from the lateral plane. Actuators are not meant to handle lateral forces at all so if it experiences any lateral forces, it will likely damage the actuator or bend the rod. So it's advised never to use lateral forces and always make sure the actuator is fully in line or in sync with your application, so it does not take any load other than the axial load. Watch the video.