- Introdução ao funcionamento dos Atuadores
- Mecanismos de Feedback Posicional
- Tipos de sistemas de controle para atuadores
- Feedback e correção de erros
- Caixas de controle para atuadores lineares
Introdução ao funcionamento dos Atuadores
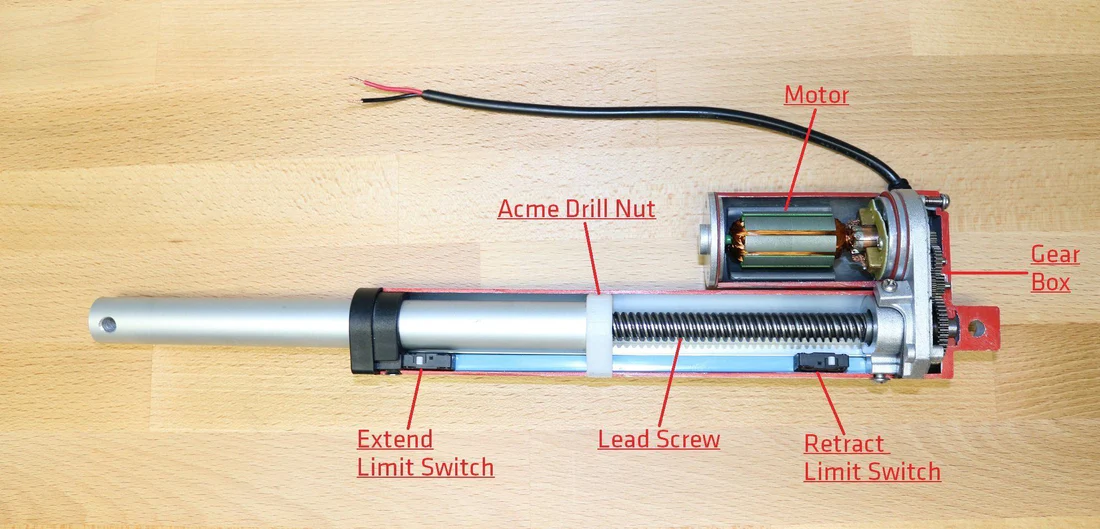
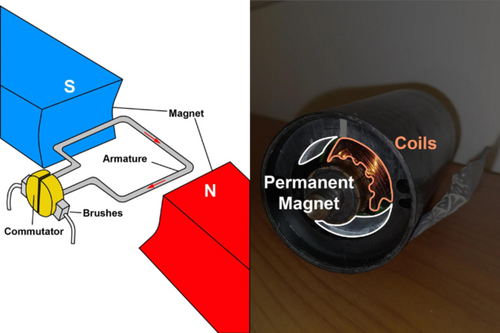
Em electric linear actuators, Corrente elétrica é usada para produzir movimento rotacional em um Motor elétrico
que é ligado mecanicamente a uma caixa de engrenagens e utiliza um lead
screw para ciclar a haste do Atuador presa a uma porca ACME para movimento linear. Os sistemas de controle para Atuadores evoluíram significativamente ao longo dos anos, aumentando a versatilidade e a funcionalidade desses dispositivos. Atuadores lineares podem ser operados por vários meios e mecanismos de controle, incluindo:
• Controladores sem fio - oferecem ao usuário a conveniência de operação por controle remoto à distância, sem a necessidade de cabos físicos.
• Controladores com Wi‑Fi e Bluetooth - permitem integração a sistemas inteligentes e acesso por dispositivos móveis, oferecendo interfaces amigáveis e a capacidade de ajustar configurações remotamente e com precisão.
Esses avanços na tecnologia de Atuadores e nos sistemas de controle ampliaram o escopo de suas aplicações, tornando-os indispensáveis em sistemas automatizados modernos. Seja ajustando janelas em veículos, operando equipamentos agrícolas pesados ou automatizando eletrodomésticos, os Atuadores continuam sendo fundamentais para traduzir sinais elétricos em ação física.

Entendendo sistemas de controle para atuadores
The primary purpose of these systems is to ensure that actuators perform accurately, efficiently, and reliably according to predefined parameters.
The significance of control systems in actuator operation cannot be overstated, particularly when it comes to achieving precise and efficient motion control. These systems are crucial for several reasons:
1. Precision: Control systems allow for the fine-tuning of actuator movements to achieve high levels of repeatability and accuracy. This is essential in applications where exact positioning is critical, such as in robotic surgery or aerospace engineering.
2. Efficiency: By optimizing the way actuators respond to commands, control systems reduce energy consumption and minimize wear and tear. This not only extends the lifespan of the actuator but also enhances the overall efficiency of the system it operates within.
3. Adaptability: Feedback mechanisms can adjust the behavior of compatible actuators in real-time by analyzing the positional feedback from compatible actuators. This adaptability is vital in dynamic environments where conditions change rapidly, such as in automated manufacturing processes or when multiple actuators are experiencing unequal weight distribution.
5. Recursos de segurança: Recursos de segurança programados, como proteção contra sobrecarga, ajudam a evitar danos a um atuador ou à aplicação interrompendo a operação após a caixa de controle detectar um consumo de corrente elétrica excessivamente alto. Outro recurso de segurança encontrado em control boxes inclui proteção contra superaquecimento para parar a operação após um determinado tempo de ciclos, garantindo que a operação permaneça dentro das classificações de ciclo de trabalho de um atuador, evitando assim a queima do motor. Os sistemas de controle são fundamentais para a funcionalidade dos atuadores, fornecendo a inteligência e a adaptabilidade necessárias para garantir precisão, eficiência, segurança e controle de movimento eficaz. Seu papel é crucial no campo em expansão da tecnologia de automação, onde a precisão de movimento costuma ser a base do sucesso operacional.
Componentes e tipos de sistemas de controle
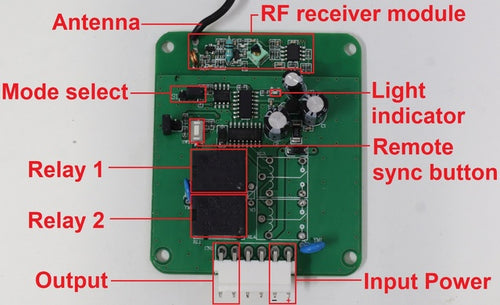
Key Components of a Basic Control Box
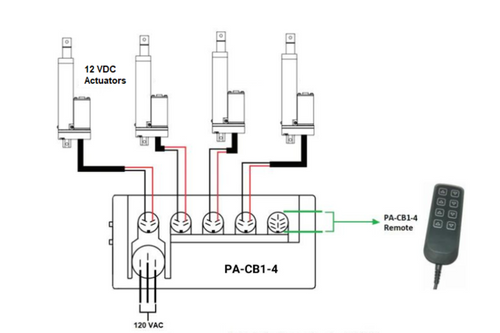
In a basic control box designed for electric linear actuators, each component plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation. Here’s a breakdown of these major components, their functions, and the purposes they serve:1. Relays: Relays act as switches that control the high-power electrical circuit using a low-power signal. For control boxes designed to manage 2-wire actuators, two relays are essential for reversing the polarity of the voltage applied across the actuator’s two wires, which in turn changes the direction of the movement. This allows for bidirectional control in a simple setup to extend and retract the actuator.
2. Input Channels: Input channels are interfaces through which the control system receives electrical signals from external sources such as power supplies or signals from wired remotes. Control boxes that operate with positional feedback may also receive input from the sensors of an actuator. These channels process the inputs from the user and/or sensors to determine how the actuator should operate, making them fundamental for initiating and controlling actuator movements based on specific requirements.
3. Output Channels: Output channels deliver control signals from the controller to the actuator or other components like relays. Control boxes that operate with positional feedback may also output electric current so that the sensors of an actuator have the power to operate. These channels are crucial for executing the commands determined by the control system, directly influencing the actuator’s behavior.
4. Remote Sync Button: This button is used to synchronize the control system with a remote control device. It ensures that the remote inputs are recognized and processed by the control system, facilitating convenient and flexible operation from a distance.
5. Light Indicator: Light indicators provide visual feedback about the system’s status. They can be an indicator for power on/off, operation modes, error states, or signal reception, which helps in monitoring and troubleshooting the system without needing complex diagnostic tools.
6. Mode Select: This feature allows the user to switch between different operating modes of the control box, such as momentary or non-momentary controls. In momentary mode, a remote’s button must be continuously held in the active position for the device to operate. Once you release the switch, the device stops functioning. Non-momentary mode works like a switch that remains in its last set position until it is changed again, regardless of whether it is being pressed. This means that once activated, the device continues to operate until the switch is manually turned off.
7. Antenna: The antenna is part of control boxes that have a wireless communication setup. Antennas are used to enhance the signal range and quality between the control system and remote control devices or between interconnected systems. It is crucial for maintaining robust communication in environments where direct wiring is impractical or undesirable.
8. RF Receiver Module: This module receives radio frequency signals sent by wireless remote controls. It decodes these signals into actionable commands that the control system can understand and act upon. The RF receiver module is essential for wireless control setups, allowing for remote operation of the actuator without physical contact. Together, these components form a comprehensive control system for 2-wire actuators, each serving a specific function that contributes to the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the actuator’s operation. This system not only allows for precise control over the actuator’s movements but also enhances the user interface and interaction, making it adaptable to a wide range of applications.
Mecanismos de Feedback Posicional
Hall effect sensors
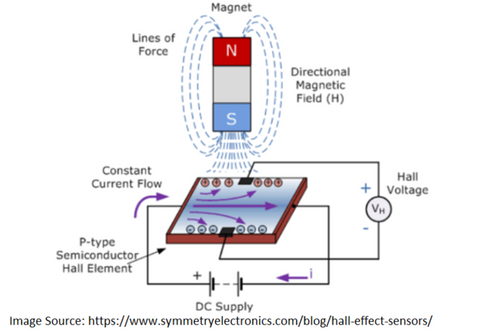
The Hall Effect theory, Edwin Hall (who discovered the Hall Effect), stated that whenever a magnetic field is applied in a direction perpendicular to the flow of electric current in a conductor, a voltage difference is induced. This voltage can be used to detect whether a hall effect sensor is in the proximity of a magnet.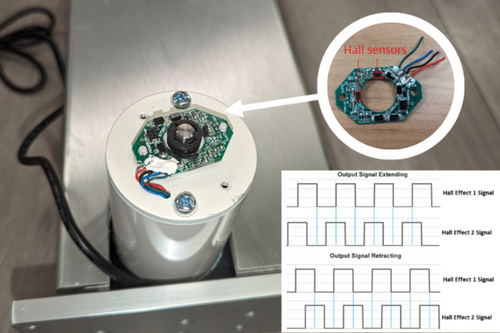

Potenciômetros
A potentiometer provides a variable resistance that is proportional to the position of the actuator. Gears are often linked between the potentiometer’s knob and the actuator’s rotating motor. As the actuator moves, the resistance value changes, which can be measured and converted into position data. This information is then used by a control system to make fine adjustments to the actuator's position, enhancing accuracy.
Feedback de Fim de curso
The purpose of limit switch feedback signals is to allow a system to determine whether the actuator has physically tripped the internal limit switches. This kind of feedback is simple and useful for applications that mainly just require information on whether the actuator has reached the fully extended or fully retracted positions.Tipos de sistemas de controle para atuadores
Um exemplo de sistema simples em malha aberta inclui uma chave basculante momentânea ligada a um atuador linear. Isso exige que um operador pressione e mantenha a chave pressionada fisicamente para que o atuador continue ciclando; soltar a chave antes de o atuador atingir o fim do percurso fará com que o atuador pare no meio do movimento.
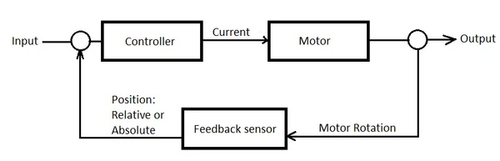
A escolha do sistema de controle e de seus componentes impacta significativamente a funcionalidade e a otimização de desempenho dos atuadores. Ao integrar mecanismos de Feedback eficazes e selecionar o tipo adequado de sistema de controle, os atuadores podem ser otimizados para uma ampla gama de aplicações, garantindo precisão e confiabilidade em sua operação.
Feedback e correção de erros
Variáveis que os sistemas de controle corrigem
1. Posição: Os sistemas de controle ajudam a garantir que um atuador atinja e mantenha com precisão a posição desejada, comparando a posição definida pelo usuário com a leitura real dos sensores de Feedback posicional. Exemplos incluem quando usuários de mesas ajustáveis pressionam um botão do controlador para que os atuadores se movam até uma predefinição de memória específica, ajustando o posto de trabalho da altura de sentado para a de pé.
2. Velocidade: Ler o Feedback posicional e dividir a distância percorrida pelo tempo decorrido resulta na velocidade de deslocamento. Alguns sistemas de controle permitem ajustar a velocidade por PWM (Modulação por Largura de Pulso), possibilitando que o atuador se mova em diferentes velocidades conforme os requisitos da aplicação. Isso é útil em aplicações que exigem velocidades variadas, como em atuadores que impulsionam o movimento de simuladores de voo.
3. Força: Certos sistemas de controle podem regular a quantidade de força exercida pelos atuadores, garantindo operação dentro de limites seguros e evitando danos ao sistema ou a componentes ao redor. Medindo o consumo de corrente elétrica, os sistemas de controle podem estimar aproximadamente quanta força está sendo exercida por atuadores lineares. Esse recurso é útil para atuadores lineares que abrem e fecham janelas, permitindo desligar a alimentação e parar a aplicação de força caso a mão de uma pessoa ou um obstáculo esteja bloqueando o percurso de movimento.
Tipos de estratégias de controle
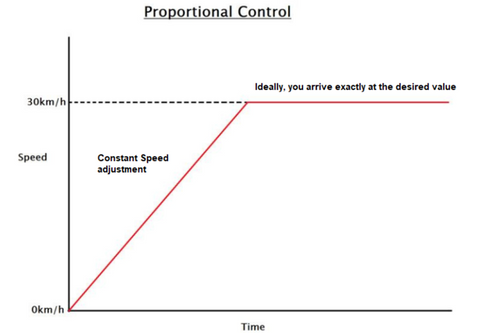
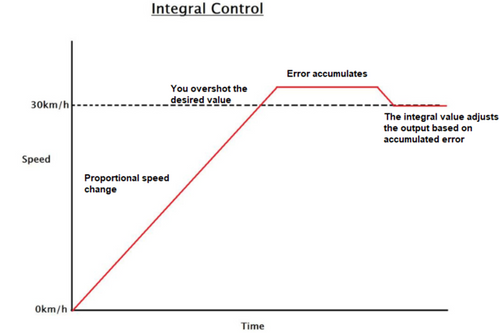
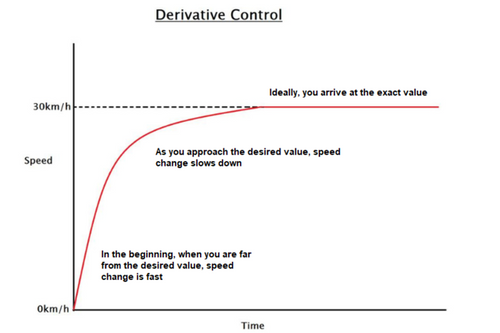
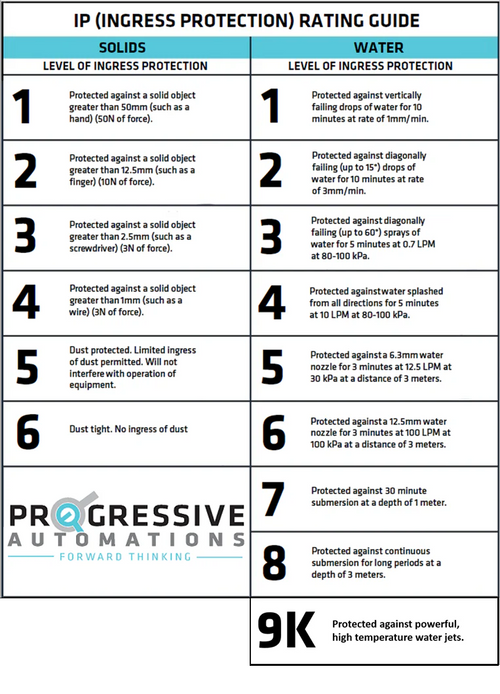
Escolhendo o sistema de controle certo
• Ingress Protection
• Compatibility
• Budget
1. Ingress Protection: Assess the specific environmental requirements of your application to determine the type of control systems needed. The PA-33 control box for example has an ingress protection rating of IP65 for dust and water resistance. An ingress protection rating of IP65 or higher is recommended for control systems exposed to outdoor elements such as rainwater, dust, and debris. 2. Compatibility: Ensure that the control system is compatible with the electric linear actuators you have chosen or are currently using to ensure seamless integration. Check if your actuator has the matching communication protocols/positional feedback to the controllers you were considering. For example, the PA-12-T (TTL/PWM) and PA-12-R (RS-485) Micro Precision Servo Actuator provide precise position control with positional accuracy up to 100 um and require advanced communication protocols for such performance. Another thing to consider is whether the type of motor your actuator has will be compatible with a control system. Continuously operating brushless motors such as those found in our custom ordered PA-14 actuators would require control boxes compatible with their operation such as the LC-241 control box. To see which of our control boxes and actuators are compatible with each other, check out our control box comparison and compatibility charts linked below: https://7717445.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/7717445/PDF%20Manuals/Desk%20Accessories/Control%20Boxes%20Compatibility%20Chart%202023.pdf https://7717445.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/7717445/PDF%20Manuals/Desk%20Accessories/Control%20Boxes%20Comparison%20Chart-1.pdf 3. Budget: Consider if there were any budget constraints for the project and choose a control system that offers the best value for your investment while meeting your performance requirements. For example, simple indoor projects that do not require high precision would work without any issues by wiring a basic rocker switch without high ingress protection to control a 2-wire mini linear actuator at an affordable price.

Caixas de controle do tipo Efeito Hall
Read our blog on applications for the FLTCON control boxes for more information.