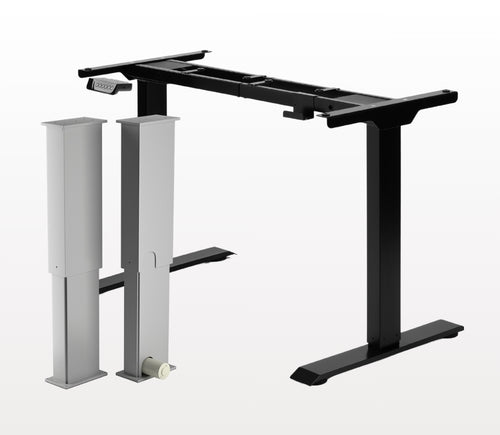
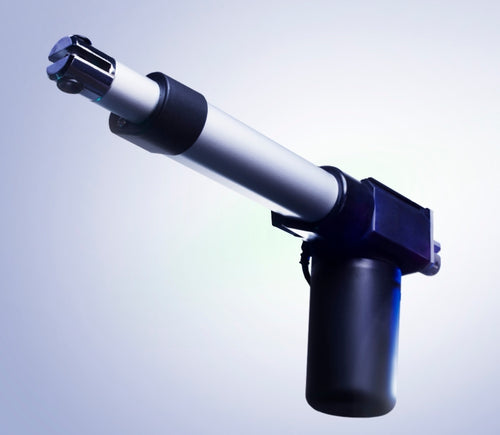
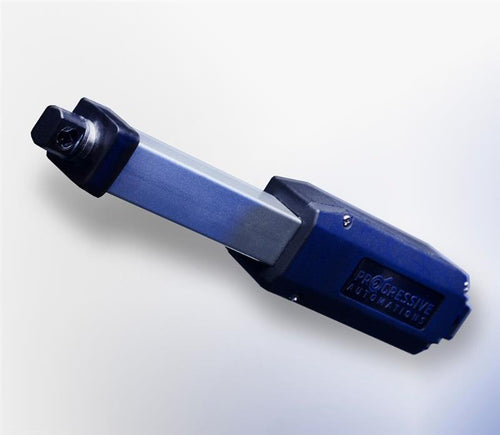
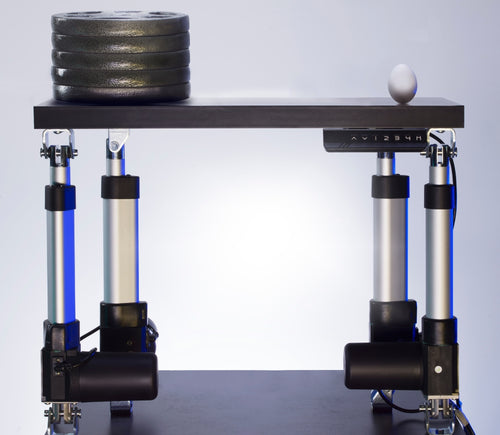
Different stroke lengths of models are available upon request, please email us at: sales@progressiveautomations.com
Ta vzorčna koda uporablja MegaMoto Plus in Arduino Uno za nadzor toka linearnega aktuatorja; uporabljeni so lahko tudi podobni izdelki kot zamenjave.
/* Koda za nadzor tokovne porabe aktuatorja in za izklop napajanja,
če preseže določeno vrednost.
Napisal Progressive Automations
19. avgust 2015
Strojna oprema:
- RobotPower MegaMoto kontrolne plošče
- Arduino Uno
- 2 potisna gumba
*/
const int EnablePin = 8;
const int PWMPinA = 11;
const int PWMPinB = 3; // pini za MegaMoto
const int buttonLeft = 4;
const int buttonRight = 5;//gumba za premik motorja
const int CPin1 = A5; // povratna zveza motorja
int leftlatch = LOW;
int rightlatch = LOW;//zapahi motorja (za logiko kode)
int hitLimits = 0;//začetek pri 0
int hitLimitsmax = 10;//vrednosti za prepoznavo, ali so bili doseženi končni položaji
long lastfeedbacktime = 0; // mora biti tip long, sicer pride do prekoračitve
int firstfeedbacktimedelay = 750; // prvi zamik za ignoriranje tokovnega sunka
int feedbacktimedelay = 50; // zamik med cikli povratne zveze, kako pogosto želite preverjati motor
long currentTimefeedback = 0; // mora biti tip long, sicer pride do prekoračitve
int debounceTime = 300; // čas za odpravo tresenja kontaktov gumbov; nižje vrednosti povečajo občutljivost
long lastButtonpress = 0; // časovnik za odpravo tresenja
long currentTimedebounce = 0;
int CRaw = 0; // vhodna vrednost za odčitke toka
int maxAmps = 0; // mejna vrednost sprožitve
bool dontExtend = false;
bool firstRun = true;
bool fullyRetracted = false;//logika programa
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(EnablePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMPinA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMPinB, OUTPUT);//nastavite izhode motorja
pinMode(buttonLeft, INPUT);
pinMode(buttonRight, INPUT);//gumba
digitalWrite(buttonLeft, HIGH);
digitalWrite(buttonRight, HIGH);//omogočite notranje pull-up upore
pinMode(CPin1, INPUT);//nastavite vhod za povratno zvezo
currentTimedebounce = millis();
currentTimefeedback = 0;//nastavite začetne čase
maxAmps = 15;// TUKAJ NASTAVITE NAJVEČJI TOK
}//konec setup
void loop()
{
latchButtons();//preverite gumba in ali je treba premakniti
moveMotor();//preverite zapaha; premaknite motor naprej ali nazaj
}//konec glavne zanke
void latchButtons()
{
if (digitalRead(buttonLeft)==LOW)//levo je naprej
{
currentTimedebounce = millis() - lastButtonpress;// preveri čas od zadnjega pritiska
if (currentTimedebounce > debounceTime && dontExtend == false)//ko se sproži dontExtend, ignoriraj vse pritiske za naprej
{
leftlatch = !leftlatch;// če se motor premika, ustavi; če stoji, začni premikati
firstRun = true;// nastavi zastavico firstRun za ignoriranje tokovnega sunka
fullyRetracted = false; // ko se premakneš naprej, ni več popolnoma uvlečeno
lastButtonpress = millis();//shrani čas zadnjega pritiska gumba
return;
}//konec if
}//konec btnLEFT
if (digitalRead(buttonRight)==LOW)//desno je nazaj
{
currentTimedebounce = millis() - lastButtonpress;// preveri čas od zadnjega pritiska
if (currentTimedebounce > debounceTime)
{
rightlatch = !rightlatch;// če se motor premika, ustavi; če stoji, začni premikati
firstRun = true;// nastavi firstRun za ignoriranje tokovnega sunka
lastButtonpress = millis();//shrani čas zadnjega pritiska gumba
return; }//konec if
}//konec btnRIGHT
}//konec latchButtons
void moveMotor()
{
if (leftlatch == HIGH) motorForward(255); //hitrost = 0-255
if (leftlatch == LOW) motorStop();
if (rightlatch == HIGH) motorBack(255); //hitrost = 0-255
if (rightlatch == LOW) motorStop();
}//konec moveMotor
void motorForward(int speeed)
{
while (dontExtend == false && leftlatch == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(EnablePin, HIGH);
analogWrite(PWMPinA, speeed);
analogWrite(PWMPinB, 0);//premakni motor
if (firstRun == true) delay(firstfeedbacktimedelay); // večji zamik za ignoriranje tokovnega sunka
else delay(feedbacktimedelay); //manjši zamik za dosego hitrosti
getFeedback();
firstRun = false;
latchButtons();//ponovno preveri gumba
}//konec while
}//konec motorForward
void motorBack (int speeed)
{
while (rightlatch == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(EnablePin, HIGH);
analogWrite(PWMPinA, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB, speeed);//premakni motor
if (firstRun == true) delay(firstfeedbacktimedelay);// večji zamik za ignoriranje tokovnega sunka
else delay(feedbacktimedelay); //manjši zamik za dosego hitrosti
getFeedback();
firstRun = false;
latchButtons();//ponovno preveri gumba
}//konec while
dontExtend = false;//motoru ponovno dovoli izvlek po uvleku
}//konec motorBack
void motorStop()
{
analogWrite(PWMPinA, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB, 0);
digitalWrite(EnablePin, LOW);
firstRun = true;//ko se motor ustavi, znova omogoči firstRun zaradi začetnih tokovnih sunkov
}//konec stopMotor
void getFeedback()
{
CRaw = analogRead(CPin1); // Preberite tok
if (CRaw == 0 && hitLimits < hitLimitsmax) hitLimits = hitLimits + 1;
else hitLimits = 0; // preveri, ali je motor na končnih položajih in se je tok ustavil
if (hitLimits == hitLimitsmax && rightlatch == HIGH)
{
rightlatch = LOW; // ustavi motor
fullyRetracted = true;
}//konec if
else if (hitLimits == hitLimitsmax && leftlatch == HIGH)
{
leftlatch = LOW;//ustavi motor
hitLimits = 0;
}//konec if
if (CRaw > maxAmps)
{
dontExtend = true;
leftlatch = LOW; //ustavi, če je povratna zveza nad največjo
}//konec if
lastfeedbacktime = millis();//shrani prejšnji čas za prejem povratne zveze
}//konec getFeedback
Ta vzorčna koda prikazuje, kako z Arduino Uno in LC-82 MultiMoto Arduino Shield upravljati do 4 naših linearnih aktuatorjev; kot zamenjave se lahko uporabijo tudi podobni izdelki. Koda je namenjena le modelom aktuatorjev, ki so znotraj tokovnih omejitev posameznega kanala MultiMoto, kot sta PA-14 in PA-14P.
/* Vzorčna koda za upravljanje do 4 aktuatorjev z gonilnikom Robot Power MultiMoto.
Strojna oprema:
- Robot Power MultiMoto
- Arduino Uno
Ožičenje:
- Aktuatorje povežite na priključke M1, M2, M3, M4 na plošči MultiMoto.
- Negativni (črn) povežite na desni priključek, pozitivni (rdeč) na levi.
- Na sponke BAT priključite 12-voltni vir (najmanj 1 A na motor brez obremenitve, 8 A na motor pri polni obremenitvi). Poskrbite, da sta plus in minus povezana pravilno.
Kodo je prilagodil Progressive Automations iz vzorčne kode, ki jo je zagotovil Robot Power
<a href="http://www.robotpower.com/downloads/" rel="nofollow"> http://www.robotpower.com/downloads/</a>
Robot Power MultiMoto v1.0 demo
Ta programska oprema je objavljena v javni domeni
*/
// vključite knjižnico SPI:
#include <SPI.h>
// L9958 pin-i za izbiro sužnja (slave select) za SPI
#define SS_M4 14
#define SS_M3 13
#define SS_M2 12
#define SS_M1 11
// L9958 pini za smer
#define DIR_M1 2
#define DIR_M2 3
#define DIR_M3 4
#define DIR_M4 7
// L9958 PWM pini
#define PWM_M1 9
#define PWM_M2 10 // Timer1
#define PWM_M3 5
#define PWM_M4 6 // Timer0
// L9958 Enable za vse 4 motorje
#define ENABLE_MOTORS 8
int pwm1, pwm2, pwm3, pwm4;
boolean dir1, dir2, dir3, dir4;
void setup() {
unsigned int configWord;
// tukaj postavite nastavitveno kodo; zažene se enkrat:
pinMode(SS_M1, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M1, LOW); // HIGH = ni izbran
pinMode(SS_M2, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M2, LOW);
pinMode(SS_M3, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M3, LOW);
pinMode(SS_M4, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SS_M4, LOW);
// L9958 pini za smer
pinMode(DIR_M1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_M2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_M3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_M4, OUTPUT);
// L9958 PWM pini
pinMode(PWM_M1, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M1, LOW);
pinMode(PWM_M2, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M2, LOW); // Timer1
pinMode(PWM_M3, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M3, LOW);
pinMode(PWM_M4, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PWM_M4, LOW); // Timer0
// L9958 Enable za vse 4 motorje
pinMode(ENABLE_MOTORS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ENABLE_MOTORS, HIGH); // HIGH = onemogočeno
/ /******* Nastavitev čipov L9958 *********
' L9958 Config Register
' Bit
'0 - RES
'1 - DR - reset
'2 - CL_1 - omejitev toka
'3 - CL_2 - omejitev toka
'4 - RES
'5 - RES
'6 - RES
'7 - RES
'8 - VSR - hitrost spreminjanja napetosti (1 omogoči omejitev, 0 onemogoči)
'9 - ISR - hitrost spreminjanja toka (1 omogoči omejitev, 0 onemogoči)
'10 - ISR_DIS - onemogoči omejitev hitrosti spreminjanja toka
'11 - OL_ON - omogoči odprto breme
'12 - RES
'13 - RES
'14 - 0 - vedno nič
'15 - 0 - vedno nič
*/ // nastavi na največjo omejitev toka in onemogoči ISR omejevanje hitrosti
configWord = 0b0000010000001100;
SPI.begin();
SPI.setBitOrder(LSBFIRST);
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE1); // ura pol. = nizko, faza = visoka
// Motor 1
digitalWrite(SS_M1, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M1, HIGH);
// Motor 2
digitalWrite(SS_M2, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M2, HIGH);
// Motor 3
digitalWrite(SS_M3, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M3, HIGH);
// Motor 4
digitalWrite(SS_M4, LOW);
SPI.transfer(lowByte(configWord));
SPI.transfer(highByte(configWord));
digitalWrite(SS_M4, HIGH);
//Začetne nastavitve aktuatorjev: zaradi varnosti uvlečeno pri hitrosti 0
dir1 = 0; dir2 = 0; dir3 = 0; dir4 = 0; // nastavi smer
pwm1 = 0; pwm2 = 0; pwm3 = 0; pwm4 = 0; // nastavi hitrost (0–255)
digitalWrite(ENABLE_MOTORS, LOW);// LOW = omogočeno
} // Konec setup
void loop() {
dir1 = 1;
pwm1 = 255; // nastavi smer in hitrost
digitalWrite(DIR_M1, dir1);
analogWrite(PWM_M1, pwm1); // zapis na pine
dir2 = 0;
pwm2 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M2, dir2);
analogWrite(PWM_M2, pwm2);
dir3 = 1;
pwm3 = 255;
digitalWrite(DIR_M3, dir3);
analogWrite(PWM_M3, pwm3);
dir4 = 0;
pwm4 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M4, dir4);
analogWrite(PWM_M4, pwm4);
delay(5000); // počakaj, ko so vsi štirje motorji nastavljeni
dir1 = 0;
pwm1 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M1, dir1);
analogWrite(PWM_M1, pwm1);
dir2 = 1;
pwm2 = 255;
digitalWrite(DIR_M2, dir2);
analogWrite(PWM_M2, pwm2);
dir3 = 0;
pwm3 = 128;
digitalWrite(DIR_M3, dir3);
analogWrite(PWM_M3, pwm3);
dir4 = 1;
pwm4 = 255;
digitalWrite(DIR_M4, dir4);
analogWrite(PWM_M4, pwm4);
delay(5000);
}//konec void loop
Ta vzorčna koda združuje enokanalni regulator hitrosti Wasp z Arduino Uno za upravljanje gibanja linearnega aktuatorja; kot zamenjave se lahko uporabijo tudi podobni izdelki.
/*Vzorčna koda za Robot Power Wasp.
Ta ESC se upravlja z RC-signali s pulzi
v razponu 1000–2000 mikrosekund.
Glavna zanka tega programa drži aktuator 1 sekundo pri miru, 2 sekundi izteguje,
ustavi za 1 sekundo, 2 sekundi uvleče in ponavlja.
Prilagojeno pri Progressive Automations na osnovi izvirne vzorčne kode "Sweep" iz
Arduino knjižnic.
Strojna oprema:
- 1 krmilnik Wasp
- Arduino Uno
Ožičenje:
Nadzorna stran:
- Rdečo/črno povežite na +5 V in GND
- Rumeno žico povežite s signalnim pinom na Arduinu (v tem primeru pin 9)
Močnostna stran:
- +/- napajalnika motorja povežite na +/- priključke na Wasp
- +/- aktuatorja povežite na preostala dva priključka
Ta vzorčna koda je v javni domeni.
*/
#include <servo.h>
Servo myservo; // ustvarite objekt servo za upravljanje servomotorja
// na večini plošč je mogoče ustvariti dvanajst servo objektov
int pos = 0; // spremenljivka za shranjevanje položaja serva
void setup()
{
myservo.attach(9); // servo na pinu 9 poveže z objektom servo
}
void loop()
{
myservo.writeMicroseconds(1500); // signal za ustavitev
delay(1000); // 1 sekunda
myservo.writeMicroseconds(2000); // signal: polna hitrost naprej
delay(2000); // 2 sekundi
myservo.writeMicroseconds(1500); // signal za ustavitev
delay(1000); // 1 sekunda
myservo.writeMicroseconds(1000); // signal: polna hitrost nazaj
delay(2000); // 2 sekundi
}
Ta vzorčna koda uporablja naše releje in Arduino Uno za upravljanje linearnega aktuatorja; kot zamenjave se lahko uporabijo tudi podobni izdelki. Več podrobnosti si lahko preberete v našem blog prispevku.
const int forwards = 7;
const int backwards = 6;//dodeli pin INx releja Arduino pinu
void setup() {
pinMode(forwards, OUTPUT);//nastavi rele kot izhod
pinMode(backwards, OUTPUT);//nastavi rele kot izhod
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(forwards, LOW);
digitalWrite(backwards, HIGH);//Aktiviraj rele v eno smer; ravni morajo biti različni, da se motor premika
delay(2000); // počakaj 2 sekundi
digitalWrite(forwards, HIGH);
digitalWrite(backwards, HIGH);//Deaktiviraj oba releja za zaviranje motorja
delay(2000);// počakaj 2 sekundi
digitalWrite(forwards, HIGH);
digitalWrite(backwards, LOW);//Aktiviraj rele v drugo smer; ravni morajo biti različni, da se motor premika
delay(2000);// počakaj 2 sekundi
digitalWrite(forwards, HIGH);
digitalWrite(backwards, HIGH);//Deaktiviraj oba releja za zaviranje motorja
delay(2000);// počakaj 2 sekundi
}
Ta vzorčna koda uporablja naš LC-80, Arduino Uno, katerikoli linearni aktuator in vir napajanja; kot zamenjave se lahko uporabijo tudi podobni izdelki. Več podrobnosti o kodi in njenem delovanju najdete v našem blog prispevku.
//Uporabite jumpers na plošči za izbiro, kateri pini bodo uporabljeni
int EnablePin1 = 13;
int PWMPinA1 = 11;
int PWMPinB1 = 3;
int extendtime = 10 * 1000; // 10 sekund, krat 1000 za pretvorbo v milisekunde
int retracttime = 10 * 1000; // 10 sekund, krat 1000 za pretvorbo v milisekunde
int timetorun = 300 * 1000; // 300 sekund, krat 1000 za pretvorbo v milisekunde
int duty;
int elapsedTime;
boolean keepMoving;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(EnablePin1, OUTPUT);//omogoči ploščo
pinMode(PWMPinA1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMPinB1, OUTPUT);//nastavi izhode motorja
elapsedTime = 0; // nastavi čas na 0
keepMoving = true; //sistem se bo premikal
}//konec setup
void loop() {
if (keepMoving)
{
digitalWrite(EnablePin1, HIGH); // omogoči motor
pushActuator();
delay(extendtime);
stopActuator();
delay(10);//majhen zamik pred uvlekom
pullActuator();
delay(retracttime);
stopActuator();
elapsedTime = millis();//koliko časa je minilo?
if (elapsedTime > timetorun) {//če je minilo 300 sekund, ustavi
Serial.print("Elapsed time is over max run time. Max run time: ");
Serial.println(timetorun);
keepMoving = false;
}
}//konec if
}//konec glavne zanke
void stopActuator() {
analogWrite(PWMPinA1, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB1, 0); // hitrost 0-255
}
void pushActuator() {
analogWrite(PWMPinA1, 255);
analogWrite(PWMPinB1, 0); // hitrost 0-255
}
void pullActuator() {
analogWrite(PWMPinA1, 0);
analogWrite(PWMPinB1, 255);//hitrost 0-255
}
Ta program lahko uporabite za neprekinjeno iztegovanje in uvlačenje hoda linearnega aktuatorja.
SETUP LOOP CODE
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // inicializira serijsko komunikacijo pri 9600 bitih na sekundo
pinMode(out_lim, INPUT_PULLUP); // konfigurira pin 45 kot vhodni pin
pinMode(in_lim, INPUT_PULLUP); // konfigurira pin 53 kot vhodni pin
pinMode(run_f, OUTPUT); // konfigurira pin 25 kot izhodni pin
pinMode(run_r, OUTPUT); // konfigurira pin 30 kot izhodni pin
retract(); // ob zagonu uvleče hod
delay(500);
}
void extend() // ta funkcija omogoči delovanje motorja
{
digitalWrite(run_f, LOW);
digitalWrite(run_r, HIGH);
}
void retract() // ta funkcija obrne smer motorja
{
digitalWrite(run_f, LOW);
digitalWrite(run_r, LOW);
}
void run_stop() // ta funkcija onemogoči motor
{
digitalWrite(run_f, HIGH);
digitalWrite(run_r, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
int out_lim_state = digitalRead(out_lim); // prebere končni stikali in shrani njuno vrednost
int in_lim_state = digitalRead(in_lim);
Serial.print("vrednost zunanjega končnega stikala "), Serial.println(out_lim_state); // 0 -> končno stikalo je pritisnjeno
Serial.print("vrednost notranjega končnega stikala "), Serial.println(in_lim_state); // 1 -> končno stikalo ni pritisnjeno
if (out_lim_state == 0 && in_lim_state == 1) // če je zunanje končno stikalo pritisnjeno in notranje ne (popolnoma iztegnjeno)
{
retract(); // uvleci hod
}
else if (out_lim_state == 1 && in_lim_state == 0) // če je notranje končno stikalo pritisnjeno in zunanje ne (popolnoma uvlečeno)
{
extend(); // iztegni hod
}
else // sicer ne naredi nič
{
}
delay(5); // zamik med branji za stabilnost
}
We have data sheets, user manuals, 3D models, wiring diagrams and more in our Resources and Learning Center sections.
Depending on your application, there are different specification requirements you should consider when determining the linear actuator you need. These requirements include force, stroke, speed and mounting dimensions. For detailed actuator information, you can refer to either the datasheet or the specification table located on the selected actuator's product page. You can also contact us to speak with one of our expert engineers.
Duty cycle is the fraction of the working period in which a linear actuator can remain active. You can calculate the duty cycle of a linear actuator by using the following equation: Duty cycle (%) = (Time the linear actuator is active) / (Time for one working period)
For example: With a 25% duty cycle, an actuator can run for 5 minutes continuously before needing to rest for 15 minutes before operating.
Yes, our actuators can be seamless replacements for most applications. Please contact us if you are unsure of which actuator to opt for. You will need to know the voltage rating, force rating, and stroke length needed before we can give a recommendation for a replacement actuator.
Stroke is the travel distance of the extending rod. To find the stroke length you require, measure your application from the fully retracted position to the fully extended position. The difference will equal the stroke length you require.
We always recommend purchasing an actuator with a higher force rating than what the application requires. If unsure of your force requirements, this article may help you calculate this: How to Calculate Force to Find the Right Linear Actuator
Yes. However, it is important to have sufficient voltage and current to be applied to your actuator. Here is an article that may help you further: How to Choose the Right Power Supply for your Linear Actuator
To achieve synchronous motion control, you will require feedback. We offer feedback in the forms of internal limit switches, potentiometers, or hall effect sensors. The following article highlights some Progressive Automations' products that can be used for synchronized control: Controlling Multiple Linear Actuators at the Same Time
There are a number of reasons your linear actuator may be exerting a large amount of noise including over-force, side loading or potential water infiltration. However, it may also be the case that your actuator is simply a high-force rated actuator and therefore has a loud operating noise level. For information on how to possibly overcome this loud noise, please click here. If you are concerned there may be an issue with your actuator, please contact us.
Most of our linear actuators are available for customization. Please refer to your desired product’s datasheet to view the full capabilities of its custom options. Please note there will be a lead time of approximately 20 – 25 business days for production, excluding shipping time. There will also be an additional fee for each actuator that is modified. To find out more about custom orders, please contact us at 1800 – 676 – 6123.
Yes, this is possible. However, it does depend on the units you are currently using. To synchronize actuators, they require a form of feedback such as a potentiometer or hall effect sensors. For more information, see below some of our key content regarding linear actuator synchronization.
Presently, we do not have kits available. However, if you would like a recommendation on the compatibility of certain linear actuators with control systems, please email us at sales@progressiveautomations.com with the following information:
• Required voltage rating
• Required stroke length
• Required force rating
• Dimensional limitations of your application
• Description of your application into which the actuator(s) will be installed
Temperature may be a factor in the functionality of your linear actuator. Please ensure that you use your actuator within the specifications advised in the product datasheet. If you have a specific query related to an actuator and temperature, please contact us.
To do this, please ensure the specifications for your system are compatible with the actuator’s voltage and current ratings. If these specifications align with each other, this may be possible. Please contact us if you are unsure of which actuator to opt for.
To find this information please refer to your product’s data sheet. If your linear actuator was customized, please provide us with images of the product, including your sales order number (if possible) and email this information to sales@progressiveautomations.com
Please click here for a list of 3D CAD models available.
The control box you choose should be able to provide sufficient voltage and current rating to your actuator. If you are unsure of the specifications, please contact us.
Alternatively, you can also find compatible control boxes on your selected linear actuator's product page.
To do this, please ensure the specifications for your system are compatible with the control box’s voltage and current ratings. If these specifications align, this may be possible. if you are unsure of their compatibility, please contact us.
Yes, our PA-35 can control up to four linear actuators using an android/iOS device. For more information, read our detailed article on how to use our Wi-Fi control box and App.
No. However, we have a large variety of control boxes to choose from for each actuator. Alternatively, you may also use rocker switches as a form of motion control.
Yes, however you need to ensure your control box can provide sufficient current draw and compatible voltage. Otherwise, you risk damaging your actuator(s).
As we are primarily manufacturers and distributors, we have a limited amount of sample codes available. While we cannot provide specific coding for your application, we do have a growing list of sample Arduino codes. To access these sample codes, please click here.
We have a range of AC to DC power supplies to choose from in our catalog. As the majority of our actuators are powered via 12 VDC, a 12 VDC automotive battery is also a good solution. Please ensure the connected devices will provide sufficient current to your setup.
You can use your own power supply if it provides sufficient current draw and the right voltage to your system. Otherwise, you run the risk of damaging your actuator(s) and/or control box(es).
Yes, most of our power supplies can be converted up to 230 VAC. To browse our power supply range, click here.
While possible, we recommend using the control box that is included with the lifting column sets. These control boxes are specifically programmed for the lifting columns to work in synchronous motion and using a third-party controller may compromise this.
However, our new LG-11 offers many similar characteristics to the FLT-11 and has the option to be paired with the FLTCON series of control boxes and RT-11 remote for multiple units to travel in synchronous motion. We do have dual lifting column systems available such as FLT-06 or FLT-10 that could provide you with a minimum height of 22 inches from the ground.
All of our lifting columns include control boxes and remotes to control the units. If you would like to know more about the control boxes we use, please contact us.
The only customizable feature for our table/TV lifts is the input voltage. Please note that there will be a lead time of 20 – 25 business days for production of all custom orders.
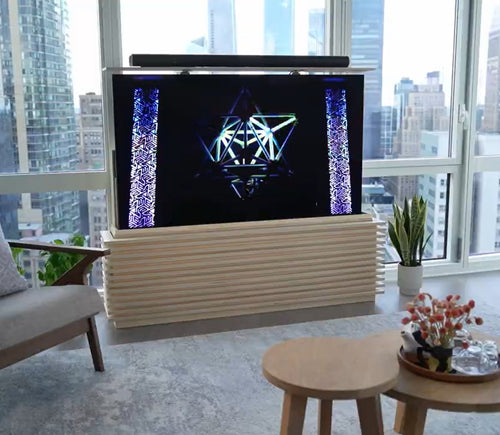
Our motorized pop-up TV lift is capable of holding up to 60-inch TV’s and our drop-down TV lifts can cater for up to 95-inch TV’s. Click here to browse our TV lifts. For even more information, check out our guide to using TV lifts.
Our table lift weight capacities are dependent on the unit you are choosing. The minimum weight capacity in our line of table lifts is 180 lbs (equal to approximately 80 kg) for our FLT-01 Single Table Lift. The maximum weight capacity in our line of table lifts is 330 lbs (equal to approximately 150 kg) for our FLT-09 Table Lift Set and FLT-05 Table Lift Set.
No, all of our mounting brackets are sold separately to our linear actuators. However, we do produce compatible mounting brackets for each of our linear actuators. To find out which mounting bracket is suitable for your linear actuator, check out your selected actuator's product page (where it will be stated), or browse our mounting bracket catalog.
For this information, please refer to our wiring diagrams.
Please email us photos of your wiring setup so we can look into this further for you. One of our sales engineers will contact you as soon as possible.
Selecting the right electric actuator for your application is a key part of bringing it to life. You need to ensure it meets all your specifications and has the ability to do exactly what you want it to do. That is why we created this handy little flowchart for selecting a linear actuator. It is broken down into four sections, with each section showing different options for our actuators so you can clearly see how they differentiate from each other:

Backdriving is when an actuator starts sliding down under load, when it is either overloaded or when the actuator has been damaged. Watch the video.
What Does Dynamic and Static Load Ratings Mean?Dynamic load rating is the amount of weight an actuator can pull or push safely when being powered. Static load rating is the amount of weight the actuator can hold or withstand without back driving when it is not being powered. For example, let's just say you have an actuator installed on a window and the static load rating of the actuator is 100lbs, it could experience backdriving when there is a high wind event, which means there will be more pressure exerted on the actuator which would exceed the 100lbs load rating of the actuator.
What Is Lateral Loading?Lateral loading is when the actuator experiences forces from the lateral plane. Actuators are not meant to handle lateral forces at all so if it experiences any lateral forces, it will likely damage the actuator or bend the rod. So it's advised never to use lateral forces and always make sure the actuator is fully in line or in sync with your application, so it does not take any load other than the axial load. Watch the video.
Orders can be placed by one of the following ways:
Online: Use our online order process with options to pay by Credit Card or PayPal.
Phone: 1-800 – 676 – 6123
Yes, quantity discounts are applied if you purchase 7 or more of the same product. Quantity discount breakdowns are found on each product page. For more information on our discount structure please contact us.
We accept all major credit cards, PayPal, checks and wire transfers. For customers who wish to set up Net Term accounts, please email us to begin the application process.
For pricing in USD, please ensure you are visiting us from our US site. For pricing in CAD, please ensure you are visiting us from our Canadian site.
All products listed on the website are in stock and available for same-day shipping if your order is placed before 3pm PST. If one of our products is unavailable, we will contact you as soon as possible to inform you when the unit will be available.
Progressive Automations’ shipping fees are calculated based on a variety of factors including but not limited to: location, quantities, and the total weight of your order. Smaller items are shipped via parcel while larger items and bulk orders are shipped via a freight carrier service. We always endeavor to provide competitive shipping prices for all our customers.
Shipping methods are available through online and phone orders. If you wish to receive an estimated shipping cost of your order, this can be done by reviewing your final shopping cart.
We ship via multiple courier companies including FedEx, UPS, DHL and USPS. Your selected courier may vary based on your location. Any large orders are shipped using various freight forwarding companies.
Please contact us if you have any questions about these options or if you would like to ship using a different carrier/your own shipping account.
Canadian and USA customers will not pay or incur any duty taxes on their orders. Customers outside North America may be subject to duty and import fees. Please contact your local government authority for information on import fees and taxes.
Returns or exchanges are accepted within 30 days of receiving your order as long as the product has not been used, modified or damaged. For more information on our return policy please see our Shipping & Returns section.
Delivery to the continental United States may take between 4 to 10 business days. All other deliveries may take approximately 10 to 15 business days depending on your location. Please refer to our shipping policy for more information: Shipping & Returns
Unfortunately, Progressive Automations does not offer free shipping. However, you can get a quantity order discount starting at 7 of the same unit.
Da, L oblikovana stoječa miza omogoča poljubno usmeritev in jo je mogoče namestiti po vaši želji. Tukaj je članek s koraki, ki pojasnjuje, kako je to mogoče: Uporabniški priročnik FLT-05
OPOMBA: Spodnji koraki se lahko razlikujejo glede na model vaše daljinske enote. Naslednja navodila so pripravljena za standardni daljinski upravljalnik RT-11. Za nastavitev največje višine okvirja se premaknite na želeno višino in sledite spodnjim korakom:
- Pritisnite M in na zaslonu se bo prikazalo [5 -]
- Pritisnite gumb UP in opazili boste, da [5 -] utripa
- Držite gumb M, dokler na zaslonu ne vidite [999]
- Največja višina je zdaj nastavljena
Za nastavitev najmanjše višine okvirja se premaknite na želeno višino in sledite spodnjim korakom:
- Pritisnite M in na zaslonu se bo prikazalo [5 -]
- Pritisnite gumb DOWN in opazili boste, da [5 -] utripa
- Držite gumb M, dokler na zaslonu ne vidite [000]
- Najmanjša višina je zdaj nastavljena
Za ponastavitev omejitev sledite spodnjim korakom:
- Pritisnite M, na zaslonu se prikaže [5 -], in spustite
- Držite M, dokler ne vidite [555]
- Omejitve so bile ponastavljene
OPOMBA: Spodnji koraki se lahko razlikujejo glede na model vaše daljinske enote. Naslednja navodila so pripravljena za standardni daljinski upravljalnik RT-11.
Če morate držati gumbe na daljincu, da dosežete prednastavljeno višino, to pomeni, da je vaša krmilna škatla v načinu momentary. Da daljinec nastavite na način non-momentary, sledite spodnjim korakom
- Prepričajte se, da ni ničesar pod mizo, saj moramo vstopiti v postopek ponastavitve
- Pritisnite in držite gumb DOWN, dokler zaslon ne prikaže [ASr]
- Ko se prikaže [ASr], pritisnite in držite [1]; prikazani sta lahko dve vrednosti:
a. 10.1 = Non-momentary Mode
b. 10.2 = Momentary Mode
- Dokončajte postopek ponastavitve tako, da držite gumb DOWN, dokler se vaša stoječa miza rahlo ne spusti in ponovno dvigne.
Naše stoječe mize imajo 3 nastavitve za zaznavanje trka, te pa lahko prilagodite svojim željam. Za nadaljevanje sledite spodnjim korakom:
- Prepričajte se, da ni ničesar pod mizo, saj moramo vstopiti v postopek ponastavitve
- Pritisnite in držite gumb DOWN, dokler zaslon ne prikaže [ASr]
- Ko se prikaže [ASr], pritisnite in držite gumb UP [ ^ ] in lahko vidite tri vrednosti:
a. 10.5 = 11 lbs
b. 10.6 = 22 lbs
c. 10.7 = 33 lbs
- Dokončajte postopek ponastavitve tako, da držite gumb DOWN, dokler se vaša stoječa miza rahlo ne spusti in ponovno dvigne.
Pripravili smo nekaj korakov za odpravljanje težav, če vidite katero od naslednjih kod napak na okvirjih s krmilnimi škatlami serije FLTCON:
Preverite kodo napake tukaj.
Če se težava po teh korakih še vedno pojavlja, se brez zadržkov obrnite na naše tehnične produktne inženirje na 1-800-676-6123, ali nam pošljite e-pošto na sales@progressiveautomations.com.