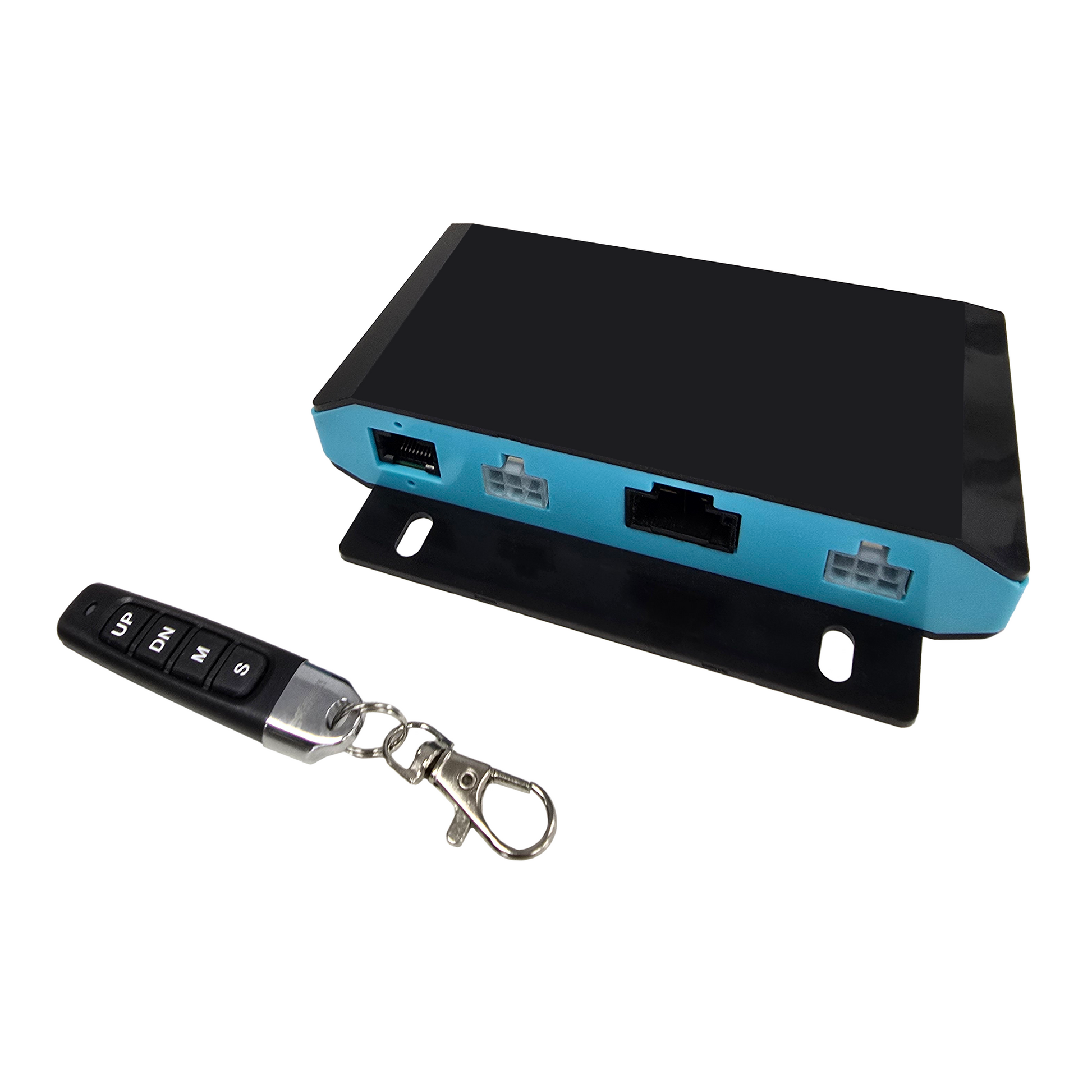
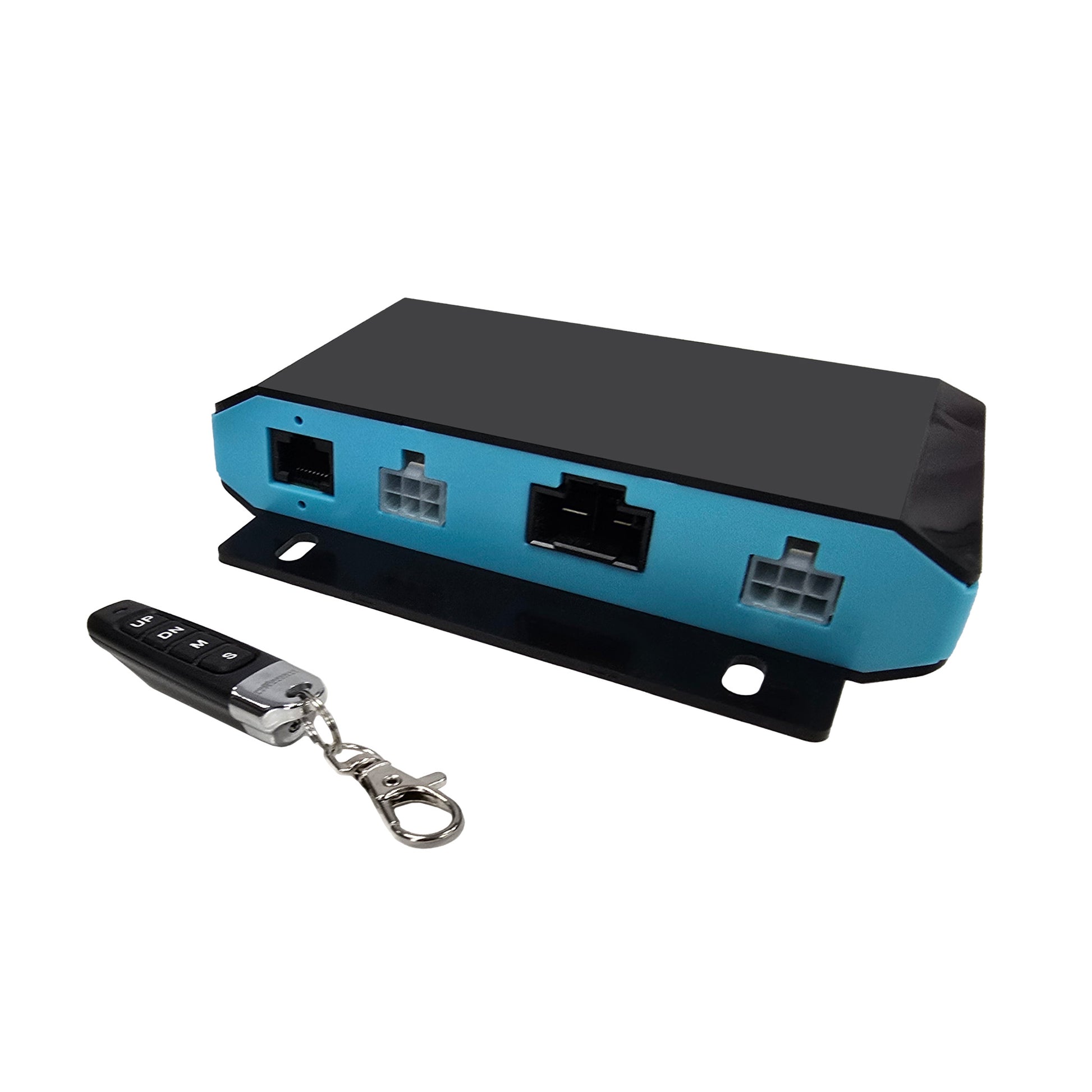
The PA-CB40-2-12V24V is Progressive Automations’ most advanced control box for synchronizing two Hall Effect Linear Actuators. It supports both 12VDC and 24VDC systems with plug-and-play compatibility for our Linear Actuators, Power Supplies, and Wiring Kits.
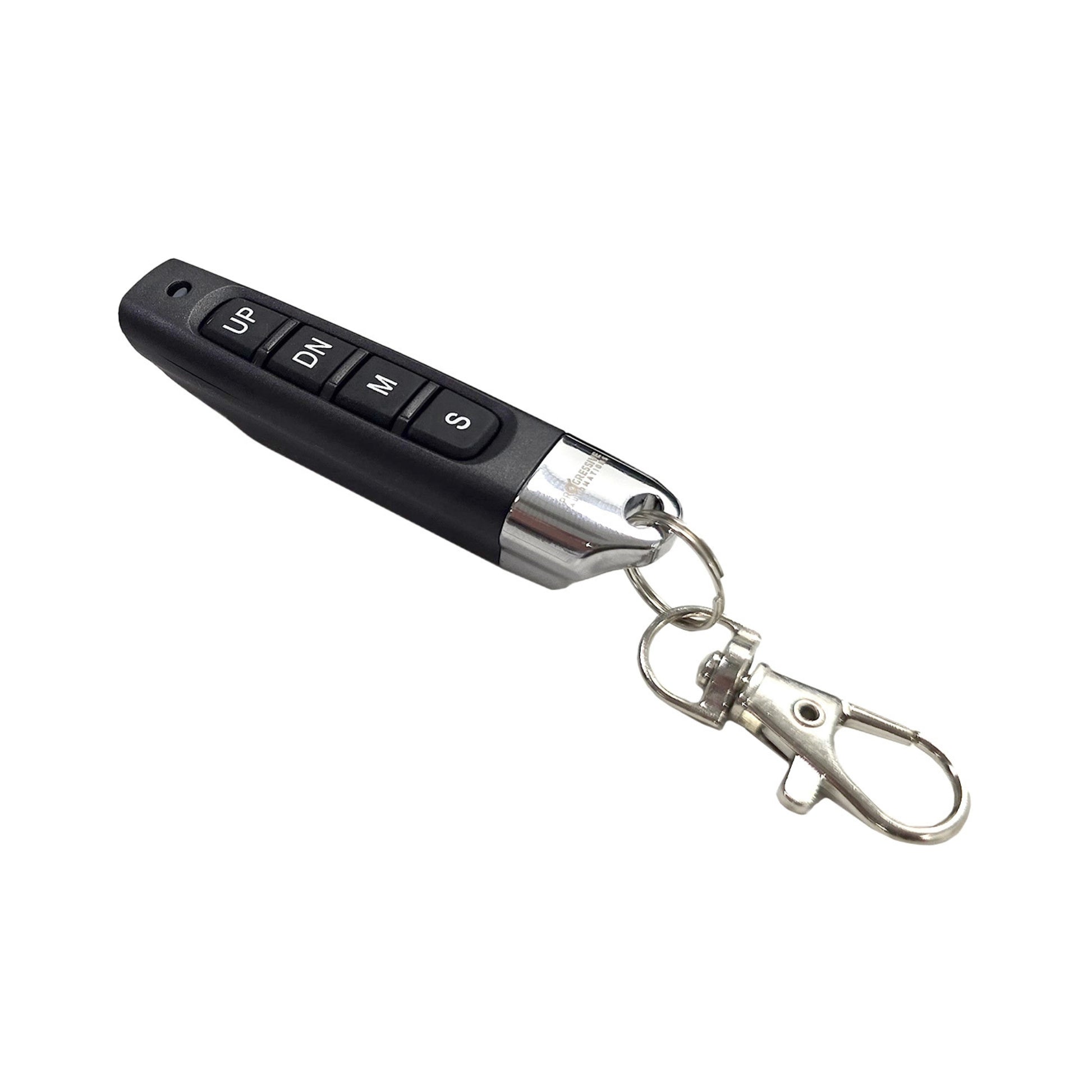
This actuator control solution features a self-learning procedure that allows pairing with a wide range of actuators within the supported range. Engineered for next-generation actuator control, it improves performance with higher power output, longer duty cycles, and faster wireless response. User experience is enhanced through simplified setup, an upgraded 4-button remote, and onboard indicators. Robust safety features include real-time sync monitoring and protection against short circuits, voltage faults, overloads, and overuse.
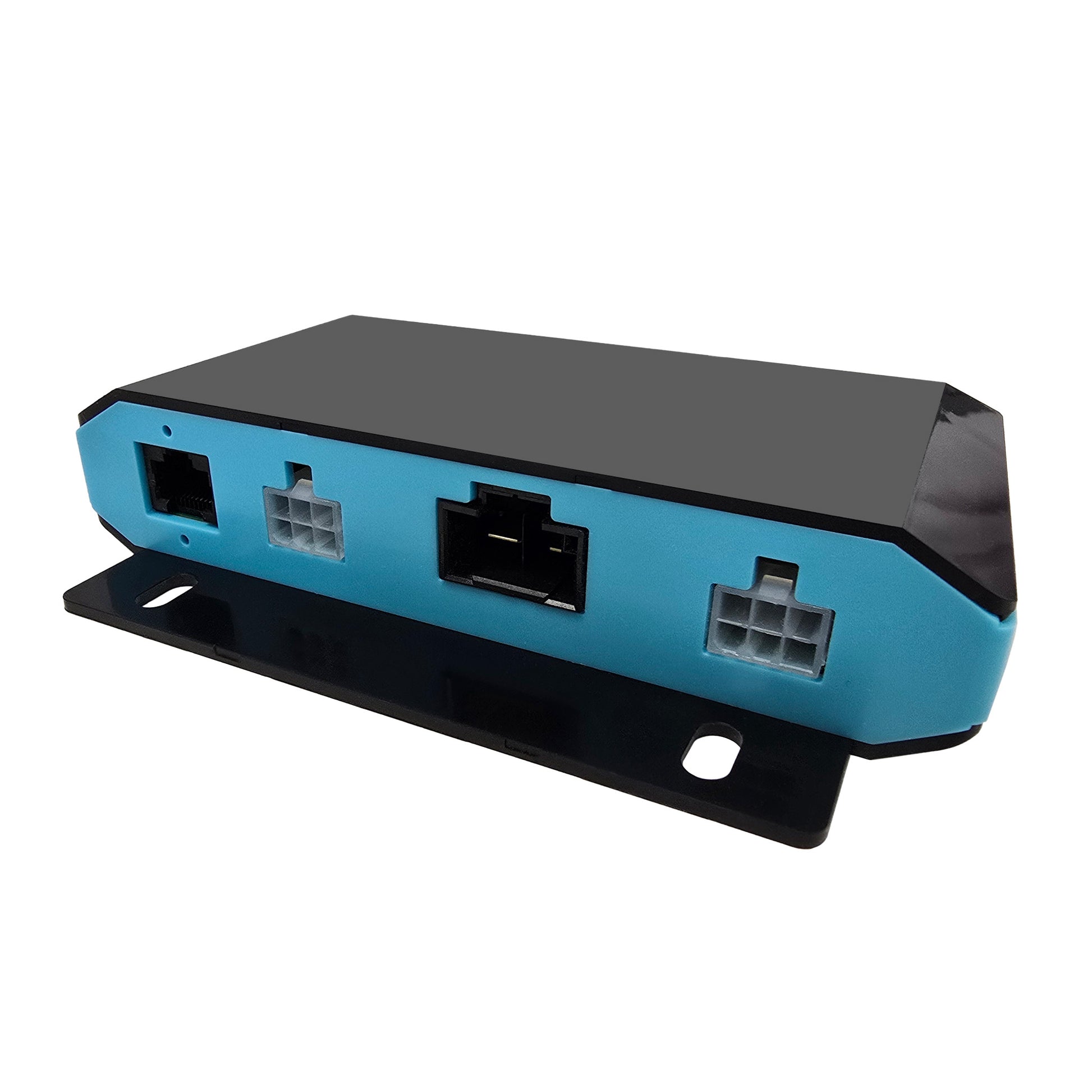
Connectivity: Plug-and-play with all load-compatible Hall Effect Linear Actuators and Power Supplies, with the appropriate wiring harness selected (sold separately). See the Compatibility section and Datasheet for more details. Please select one based on your configuration needs.
Important: This control box does not come with a wiring harness. Be sure to check your setup requirements, as the harness may need to be purchased separately.
The PA-CB40-2-12V24V is Progressive Automations’ most advanced control box for synchronizing two Hall Effect Linear Actuators. It supports both 12VDC and 24VDC systems with plug-and-play compatibility for our Linear Actuators, Power Supplies, and Wiring Kits.
This actuator control solution features a self-learning procedure that allows pairing with a wide range of actuators within the supported range. Engineered for next-generation actuator control, it improves performance with higher power output, longer duty cycles, and faster wireless response. User experience is enhanced through simplified setup, an upgraded 4-button remote, and onboard indicators. Robust safety features include real-time sync monitoring and protection against short circuits, voltage faults, overloads, and overuse.
Connectivity: Plug-and-play with all load-compatible Hall Effect Linear Actuators and Power Supplies, with the appropriate wiring harness selected (sold separately). See the Compatibility section and Datasheet for more details. Please select one based on your configuration needs.
Important: This control box does not come with a wiring harness. Be sure to check your setup requirements, as the harness may need to be purchased separately.
| Number of Channels | 2 |
| Input Voltage | 12/24VDC |
| Output Voltage | 12/24VDC |
| Current | 12.5A @12VDC Per Channel 6.25A @24VDC Per Channel |
| Duty Cycle | 25% (Max 5 minutes continuous) |
| Operational Temperature | -10°C to 50°C (14°F to 122°F) |
| Housing Color | Black/Blue |
| Housing Material | ABS Plastic |
| Kit Includes | 1x Control Box, 1x Wireless Remote (with Battery) |
| Cable Length | See compatible Power Input Cable accessories |
| Wireless Frequency | 433.92 MHz |
| Wireless Range | Minimum 100 Feet |
| Wireless Remote Functions | Up, Down, Programming Modes, Stop |
| Remote Battery Type | 12V 27A Alkaline (included) |
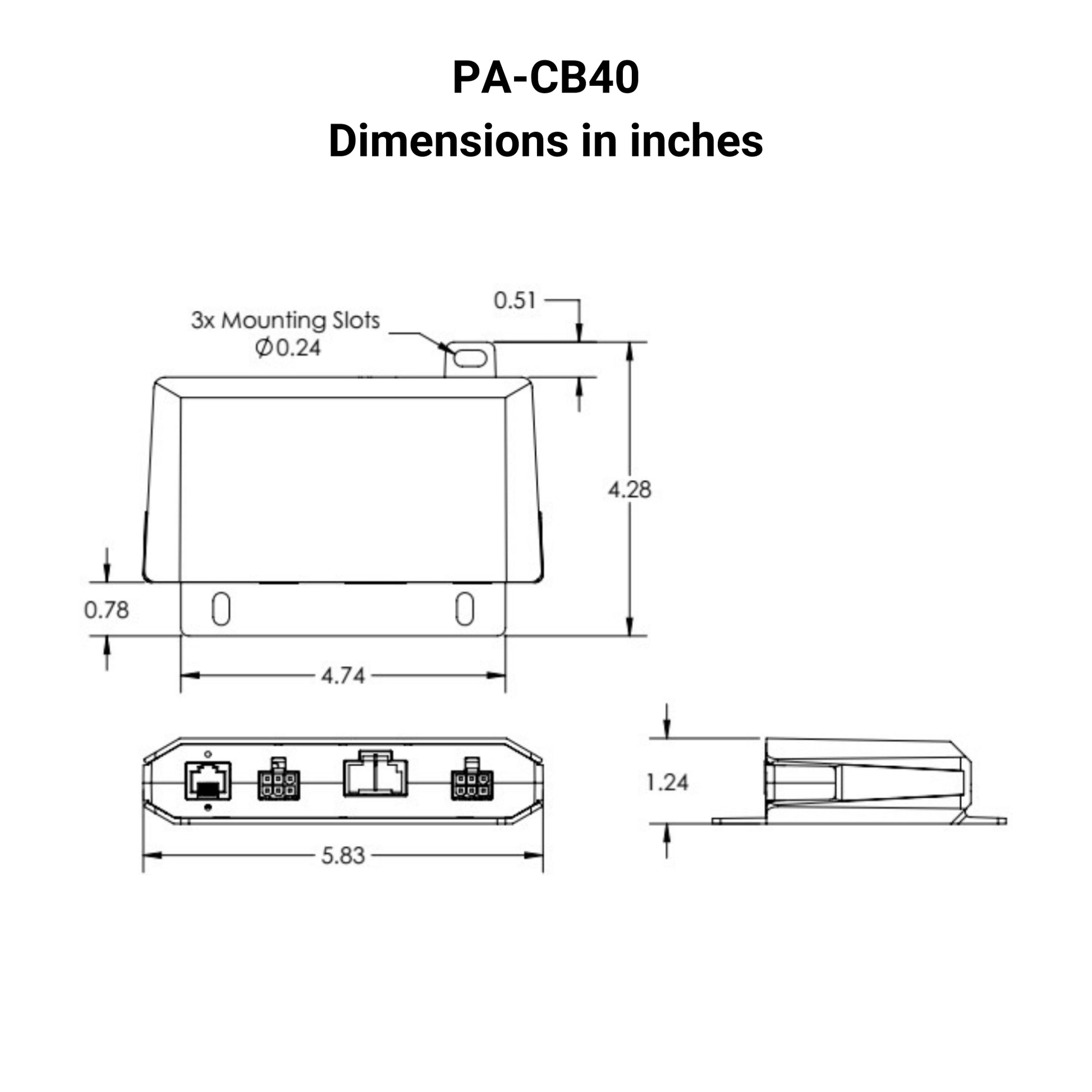
| Dimensions | 5.83" x 4.28" x 1.25" |
| Unit Weight | 0.31 lbs |
| Features |
|
| Safety Features |
|
| AC Power Option | with PS-40-12, PS-20-24 |
| Wiring Kit Options | AC-53-48, AC-52-48, AC-36-06, AC-37-48 |
Following a set of standards is crucial for businesses to ensure their products and services can meet a level of quality that promotes customer satisfaction. At Progressive Automations, we aim for nothing but the best for our customers and strive toward continual improvements. Because of this, we are excited to announce that Progressive Automations is now ISO 9001:2015 certified!
Quality Assured