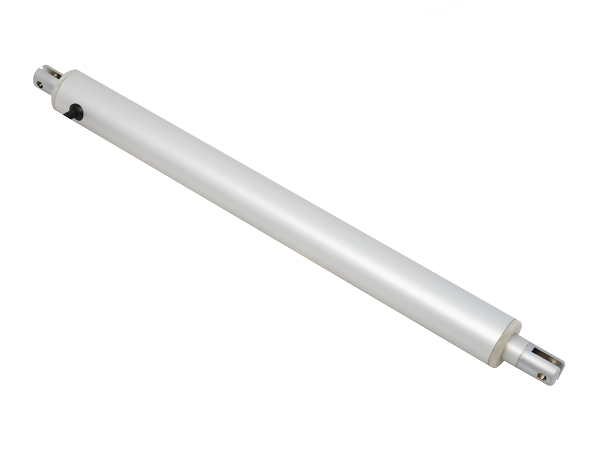
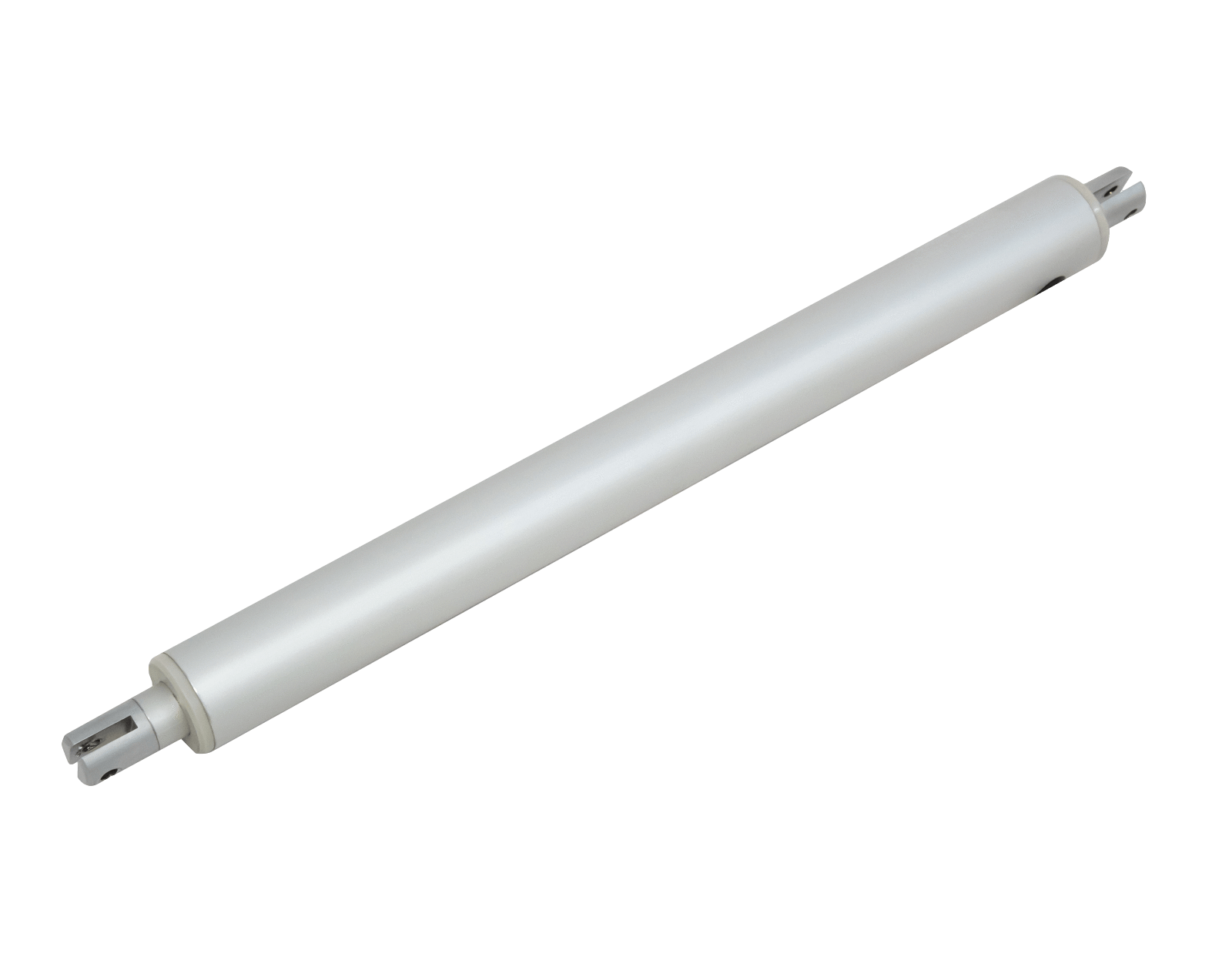
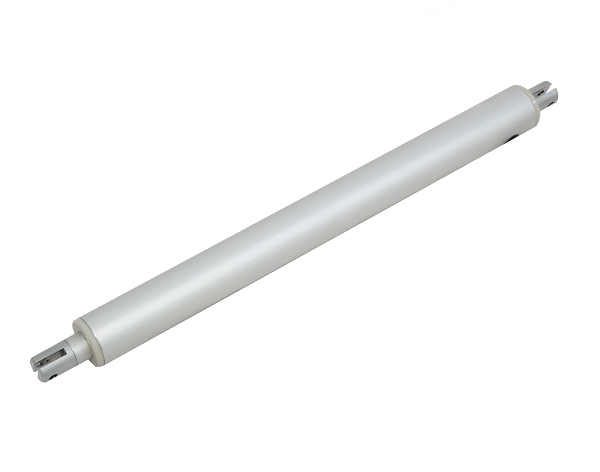
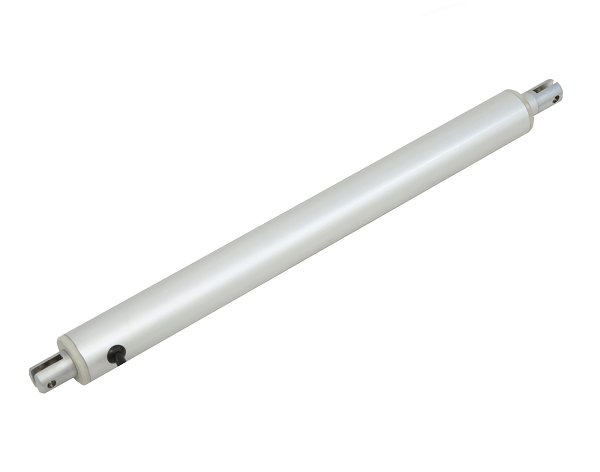
Le mini vérin linéaire tubulaire PA-11-D30 utilise une conception à moteur en ligne élancée. Combinant un faible courant nominal, cette unité peut être intégrée à la plupart des systèmes de commande basse tension. Le faible diamètre extérieur du boîtier de l'arbre et de la tige du vérin en fait une unité idéale pour les applications où l'espace est limité. Des secteurs comme l'automobile, la robotique et la domotique profitent de la conception à moteur en ligne. Pour la liste complète des spécifications, des options de personnalisation et des dessins cotés, veuillez consulter notre fiche technique PA-11-D30.
Tableau comparatif des actionneursLe mini vérin linéaire tubulaire PA-11-D30 utilise une conception à moteur en ligne élancée. Combinant un faible courant nominal, cette unité peut être intégrée à la plupart des systèmes de commande basse tension. Le faible diamètre extérieur du boîtier de l'arbre et de la tige du vérin en fait une unité idéale pour les applications où l'espace est limité. Des secteurs comme l'automobile, la robotique et la domotique profitent de la conception à moteur en ligne. Pour la liste complète des spécifications, des options de personnalisation et des dessins cotés, veuillez consulter notre fiche technique PA-11-D30.
Tableau comparatif des actionneurs| Tension d'entrée | 12VDC, 24VDC, 36VDC, 48VDC |
| Course | 1" à 24" (D30, D33), 2" à 32" (D42), 2" à 40" (D50) |
| Fonctionnalités | Aucune |
| Rétroaction | Aucune |
| Cycle de service | 20% (4 minutes en marche, 16 minutes à l'arrêt) |
| Protection contre les intempéries | IP54 |
| Protection contre les surcharges | N/A |
| Température de fonctionnement | -25ºC à 65ºC (-13ºF à 149ºF) |
| Bruit en fonctionnement | <52dB |
| Interrupteur de fin de course | Interne - Non réglable |
| Longueur du câble | 40" (personnalisable) |
| Connecteur | Molex Mini Fit Jr réceptacle 2 broches |
| Taille du trou de montage avant | 0.20" |
| Taille du trou de montage arrière | 0.20" |
| Type d'actionneur | Mini tube |
| Type de moteur | Moteur CC à balais |
| Type de vis | Vis ACME |
| Matériau de la tige | Alliage d'aluminium |
| Matériau du boîtier | Alliage d'aluminium 6062 |
| Matériau de l'engrenage | Alliage d'acier de métallurgie des poudres |
| Certifications | CE |
| Supports de montage compatibles | BRK-11 |
| Garantie | 18 mois |
Suivre un ensemble de normes est crucial pour permettre aux entreprises de garantir que leurs produits et services atteignent un niveau de qualité favorisant la satisfaction client. Chez Progressive Automations, nous visons l’excellence pour nos clients et nous nous efforçons d’apporter des améliorations continues. C’est pourquoi nous sommes ravis d’annoncer que Progressive Automations est désormais certifié ISO 9001:2015 !
Une qualité digne de confiance – En savoir plusDepending on your application, there are different specification requirements you should consider when determining the linear actuator you need. These requirements include force, stroke, speed and mounting dimensions. For detailed actuator information, you can refer to either the datasheet or the specification table located on the selected actuator's product page. You can also contact us to speak with one of our expert engineers.
Le cycle de service est la fraction de la période de fonctionnement durant laquelle un vérin linéaire peut rester actif. Vous pouvez calculer le cycle de service d’un vérin linéaire à l’aide de l’équation suivante : Cycle de service (%) = (Temps pendant lequel le vérin linéaire est actif) / (Durée d’une période de fonctionnement)
Par exemple : avec un cycle de service de 25 %, un actionneur peut fonctionner 5 minutes en continu avant de devoir se reposer 15 minutes avant de reprendre l’opération.
La course est la distance de déplacement de la tige en extension. Pour déterminer la longueur de course nécessaire, mesurez votre application de la position entièrement rétractée à la position entièrement étendue. La différence correspondra à la longueur de course requise.
Nous recommandons toujours d’acheter un actionneur avec une valeur de force supérieure à celle requise par l’application. Si vous n’êtes pas sûr de vos besoins en force, cet article peut vous aider à les calculer : Comment calculer la force pour trouver le bon vérin linéaire
Oui, c’est possible. Cependant, cela dépend des unités que vous utilisez actuellement. Pour synchroniser des actionneurs, une forme de rétroaction est nécessaire, telle qu’un potentiomètre ou des capteurs à effet Hall. Pour plus d’informations, consultez ci-dessous certains de nos contenus clés concernant la synchronisation des vérins linéaires.
Commander plusieurs vérins linéaires simultanément
Comment utiliser les boîtiers de commande FLTCON-2 & FLTCON-4 ?
The control box you choose should be able to provide sufficient voltage and current rating to your actuator. If you are unsure of the specifications, please contact us.
Alternatively, you can also find compatible control boxes on your selected linear actuator's product page.
Backdriving is when an actuator starts sliding down under load, when it is either overloaded or when the actuator has been damaged. Watch the video.
What Does Dynamic and Static Load Ratings Mean?Dynamic load rating is the amount of weight an actuator can pull or push safely when being powered. Static load rating is the amount of weight the actuator can hold or withstand without back driving when it is not being powered. For example, let's just say you have an actuator installed on a window and the static load rating of the actuator is 100lbs, it could experience backdriving when there is a high wind event, which means there will be more pressure exerted on the actuator which would exceed the 100lbs load rating of the actuator.
What Is Lateral Loading?Lateral loading is when the actuator experiences forces from the lateral plane. Actuators are not meant to handle lateral forces at all so if it experiences any lateral forces, it will likely damage the actuator or bend the rod. So it's advised never to use lateral forces and always make sure the actuator is fully in line or in sync with your application, so it does not take any load other than the axial load. Watch the video.