Guide to Micro and Mini Actuators
Efficiency, durability, and precision in a compact form factor are often highly demanded features from electric linear actuators for use in various industries and applications with space constraints. By choosing the right micro and mini actuators, applications with space constraints can experience benefits such as precision control, ease of use, and performance optimization.
This page is dedicated to understanding the fundamentals of micro and mini actuators, the advantages they offer, our range of models, critical specifications, and how to choose the best one for your specific application needs.
What Are Micro and Mini Electric Linear Actuators?

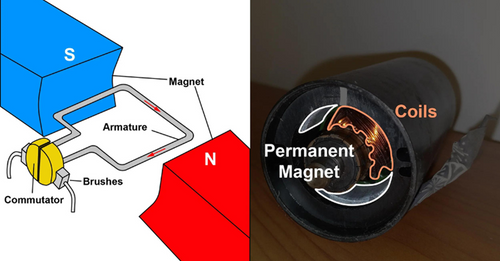
Actuators are fundamental components in various mechanical systems, playing a crucial role in energy conversion into motion. Essentially, an actuator takes an energy source, typically electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic, and converts it into a physical movement. This is achieved through different components and mechanisms depending on the type of actuator.
In electric linear actuators, electric current is used to produce rotational motion in an electric motor that’s mechanically linked to a gearbox and utilizes a lead screw to cycle the actuator’s shaft attached to an ACME drill nut for linear motion. Ball screw variants also exist, offering different benefits and drawbacks to suit other applications.
While traditional actuators can reach a bulky design, micro and mini electric linear actuators are designed to do the same job on a much smaller scale. These compact devices can fit into tight spaces and are perfect for applications where precision and subtlety are key. If chosen in a long stroke length, the width and height are the major areas that highlight the compact dimensions of micro and mini actuators.
Assuming a short stroke length of 2 inches, the width and height of micro actuators are more than compact enough for the unit to fit in the palm of your hand. Mini actuators have a larger size than micro actuators, however, mini actuators still have a compact design being approximately half or a third of the dimensional volume of standard type actuators.
Advantages of Micro and Mini Electric Linear Actuators

Micro and mini electric linear actuators offer a range of advantages that make them an indispensable part of today’s modern society. Their compact size allows for integration into tight spaces, providing precise control and movement where larger actuators do not fit.
Having a miniaturized size enhances the versatility and adaptability of the systems they are integrated with and allows for power-efficient operation from their smaller motors.
- Compact Size: Their significantly smaller width and depth allow for a form factor that can match application requirements with strict space limitations or when trying to maximize the remaining available storage space in storage compartments.
- Precision: Designed with options for positional feedback to handle applications requiring accuracy, they provide precise control over movement and have a smaller manufacturing tolerance than larger linear actuators.
- Efficiency: Despite their size, they are energy-efficient with low current draw requirements, and built-in limit switches or low power consumption when idle, making them ideal for portable systems and battery-powered devices.
- Versatility: Options for various force ratings, speeds, stroke lengths, feedback types, voltage operations, and other customizable specifications allow micro and mini actuators to be versatile in suiting a variety of settings, from medical devices to consumer electronics.
Choosing the Right Micro and Mini Actuator for Your Project
When it comes to selecting the right micro or mini actuator for your project, a few key considerations come into play:
- Load Requirements: Refers to how much force your application will require. This will influence your choice of the model actuator.
- Speed: Depending on the application, you might need a fast or slow compact actuator. Choose according to your application needs.
- Stroke Length: This is to indicate how far the actuator needs to move. Make sure to match the stroke length to your project’s travel distance requirements.
- Electrical Power Requirements: The voltage and current draw requirements of each model actuator can vary. Consider the voltage and power supply options available for your compact actuator.
- Environmental Resistance: Consider your application and the environment to determine whether your compact actuator must withstand a certain level of dust, liquid ingress, and/or corrosion.
- Positional Feedback: Determine whether your application will require a certain level of precision motion/advance capabilities or if basic manual forward and reverse control is suitable.
- Control System Compatibility: Choose control systems that are compatible with the chosen compact actuator(s). If you have pre-existing control systems, ensure the chosen actuator(s) are compatible.
We also have an online quiz with questions that can help guide you in choosing from our range of micro and mini actuators to find the most suitable model for your needs.
Load Requirements
There are a couple of factors involved in finding the right force rating to handle an application’s load requirements. Variables can include the load, the angle at which the load is being applied, and the dimensional size of the load. Load requirements are measured by how much force is required to be pushed and/or pulled directly onto the shaft of an actuator (example units: lbs, kg, Newtons)

Get free actuator testing guide
Get NowSpeed
Travel speeds usually depend on the force rating options an actuator has been configured for. Some models come with multiple force ratings options that can be selected when placing an online order. These different force rating options have their internal gear ratios adjusted to a certain torque setting that also affects the actuator's travel speed. The speed of an actuator is measured by the distance travelled over a period of time (example: inch/second, mm/second)
Stroke Length
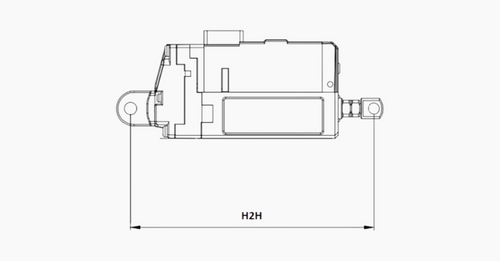
The hole-to-hole (H2H) length of an actuator measured from the center of the rear mounting hole to the center of the front mounting hole is affected by stroke length. This is because a longer stroke length requires an actuator with a longer body to house the enclosed shaft. Stroke length can be calculated by subtracting the fully closed H2H length from the fully open H2H length of the actuator (example units: inch or " for short, mm)
Electrical Power Requirements
An application may come with a pre-existing source of electrical power or will have a newly installed power supply with certain electrical power ratings and requirements. Check the voltage (VDC or VAC) and current (Ampere or A) ratings of the power source(s) and actuator(s) to verify if they are within suitable range. The general rule of thumb is that the power supply needs to have a higher current rating than the combined maximum current requirement of all the units connected to the power supply.
Environmental Resistance
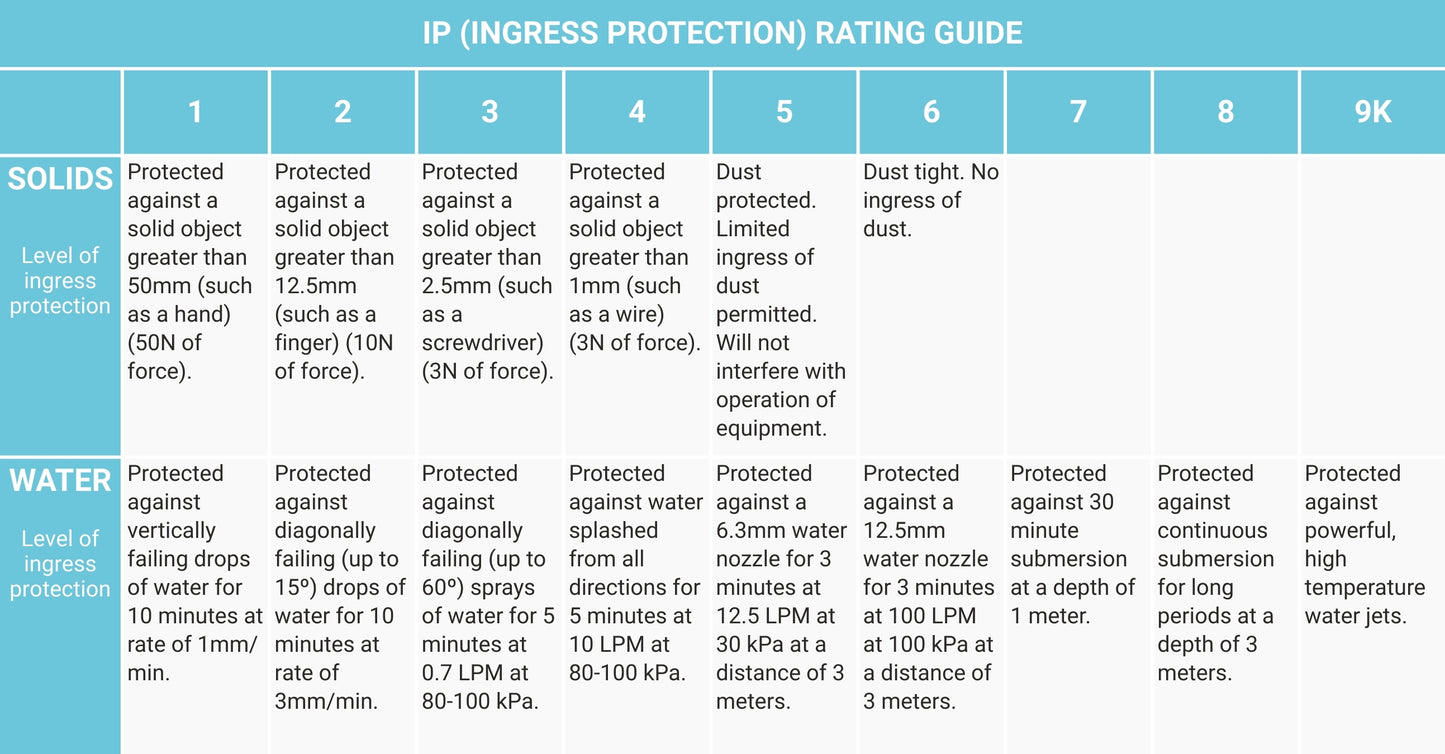
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating system uses a 2-digit system to define its protection rating for all products. The first digit represents protection against solids and the second against liquids. The IP Code was designed to standardize protection ratings and limit misinterpretation/misrepresentation of a product's protection ability. Salt spray rating is crucial for protection against corrosion that may occur from salted roads, beaches, salt water, etc.
Positional Feedback
Built-in positional feedback devices like encoders, hall effect sensors, potentiometers, etc. are used for transmitting signals that will be read by a controller to determine the position of the actuator’s stroke. This allows for capabilities such as multiple actuators that can simultaneously travel the same speed together in synchronous motion, memory presets, and/or positional display.
Control System Compatibility

Check if your actuator has the matching communication protocols/positional feedback to the controllers you were considering. For example, the PA-12-T (TTL/PWM) and PA-12-R (RS-485) Micro Precision Servo Actuator provide precise position control with positional accuracy up to 100 um and require advanced communication protocols for such performance.
Another thing to consider is whether the type of motor your actuator has will be compatible with a control system. Continuously operating brushless motors such as those found in our custom ordered PA-14 actuators would require control boxes compatible with their operation such as the LC-241 control box.
To see which of our control boxes and actuators are compatible with each other, check out our control box comparison and compatibility charts.
Programmable Functions
Control boxes such as our FLTCON series allow for the ability to have programmed functions, safety features, and other user settings that can be accessed through the connected remote control. When multiple hall effect type actuators are connected to an FLTCON control box, the control box ensures the synchronization of the motors so they move together at the same speed.
Basic Manual Controls
Consider if there were any budget constraints for the project and choose a control system that offers the best value for your investment while meeting your performance requirements. For example, simple indoor projects that do not require high precision would work without any issues by wiring a basic rocker switch without high ingress protection to control a 2-wire micro or mini linear actuator at an affordable price.
Linear actuator calculator tool
Try NowTechnical Specifications of Micro and Mini Actuators
Once the required specifications and features for a given application have been confirmed, the next step is to browse through the available models to determine which will offer the most suitable specifications for your needs. Micro actuators have certain specifications that share some overlapping similarities with mini actuators, however, the most noticeable specification difference between the two categories is usually the force rating window range.
Force Ratings
Micro actuators can range between 1.34 lbs to 39 lbs in dynamic force rating and 0.67 lbs to 56 lbs for static force ratings. Mini actuators can range from 16 lbs to 450 lbs in both dynamic and static force ratings.
| Force Rating (Micro) | PA-MC1 | PA-07 | PA-12-T | PA-12-R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic | 8 - 39 lbs | 5 lbs | 1.34 - 2.69 lbs | 3.82 - 22.48 lbs |
| Static | 8 - 56 lbs | 6.5 lbs | 0.67 - 2.69 lbs | 1.57 - 22.48 lbs |
| Force Rating (Mini) | PA-01 | PA-09 | PA-10 | PA-14 |
| Dynamic | 16 - 225 lbs | 330 lbs | 450 lbs | 35 - 150 lbs |
| Static | 16 - 225 lbs | 330 lbs | 450 lbs | 35 - 150 lbs |
Stroke Lengths
Micro actuators have a stroke length that ranges between 0.5 inch to 12 inch, while mini actuators can range between 1 inch to 40 inch. Aside from length, physical dimensions for micro actuators such as width and height will also be more compact in comparison to mini actuators.
Wireless Control, seamless motion
Get the AppSpeeds
The speed of micro actuators can range between 0.24"/sec to 2.67"/sec at full load and 0.30"/sec to 3.15"/sec at no load. Mini actuators can range between 0.16"/sec to 2.95"/sec at full load and 0.28"/sec to 3.54"/sec at no load.
| Speed (Micro) | PA-MC1 | PA-07 | PA-12-T | PA-12-R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No load | 0.31 - 1.85"/sec | 0.59"/sec | 0.47 - 1.42"/sec | 0.30 - 3.15"/sec |
| Full load | 0.24 - 1.18"/sec | 0.55"/sec | 0.35 - 0.99"/sec | 0.25 - 2.67"/sec |
| Speed (Mini) | PA-01 | PA-09 | PA-10 | PA-14 |
| No load | 0.28 - 3.54"/sec | 0.39"/sec | 0.28 - 0.56"/sec | 0.37 - 2.00"/sec |
| Full load | 0.20 - 2.95"/sec | 0.27"/sec | 0.16 - 0.33"/sec | 0.28 - 1.38"/sec |
Positional Feedback
Positional feedback and communication protocol options available for micro actuators include TTL/PWM (PA-12-T) and RS-485 (PA-12-R), while mini actuators have options including hall effect sensors (PA-09 & PA-10) and built-in potentiometer feedback (PA-14).
Each individual stock actuator can only come with one type of positional feedback or communication protocol. The type of positional feedback chosen for an actuator will affect its compatibility with existing control systems. Custom orders for certain models may have options such as limit switch feedback.
Voltage Operation
The main standard voltage option for all our mini and micro actuators is 12 VDC operations for their brushed DC motors. Options for 24 VDC are available for all mini actuators while the micro actuators have 7.4 VDC as an option for the PA-12-T. Selecting a higher voltage option tends to result in a lower current draw for the same model.
Current Draw
Micro actuators have a current draw that ranges between 200 mA to 2.3 A at full load and 30 mA to 200 mA at no load. Mini actuators draw between 2 A to 6 A at full load and 500 mA to 1.5 A at no load.
To compare our different models of micro and mini actuators, we have compiled a reference actuator comparison chart.
How To Mount Micro and Mini Electric Linear Actuators

The simplest way to ensure you have the correct mounting brackets for your linear actuator will be to source your mounting brackets from the original manufacturer of the actuator and verify they are compatible. For more information, we offer our mounting brackets compatibility chart and product descriptions under each of our actuators.
Other manufacturers may also have similar sources; however, you can also reach out for customer support as needed. For certain cases, users with unique requirements or specialized applications may have to consider custom-making their own brackets according to the measurements, design, and shape they need. Check out our actuator 3D drawings as a source for additional reference.
Equally important to sourcing compatible mounting brackets for your electric micro and mini actuators is selecting the mounting process with a method that is right for your application. Below are two common methods that are used to mount an electric linear actuator.
- Dual pivot mounting
- Stationary mounting
Dual Pivot Mounting

Dual pivot mounting is a method that involves fixing an actuator on both sides with a mounting point that is free to pivot, which usually consists of a mounting pin or a clevis. Dual pivot mounting allows the actuator to pivot on either side as it extends and retracts, allowing the application to achieve a fixed path motion with two free pivot points.
One example application of this method is to automatically open and close chicken coop doors. When the actuator extends, the dual fixed points enable the door to swing open. The action of the door closing and opening causes changes in angle, but the pivot provides ample space for the two mounting points to rotate. While using this method, make sure that there is enough room for the actuator to extend, without any obstacles on its way.
Stationary Mounting
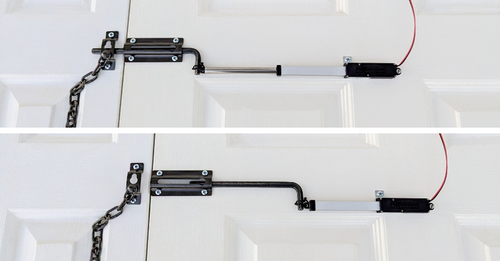
For the stationary mounting method, the shaft can extend and retract from the housing in a straight line path while the rest of the actuator is mounted in a fixed stationary position. A mounting bracket for the shaft housing may be used to help maintain the ideal alignment of the actuator in place on a mounted surface.
This kind of mounting is commonly used to achieve actions like pushing and pulling an attachment head-on. For instance, this form of mounting is ideal for pushing and pulling a sliding door latch to lock and unlock a door. When deciding on this method, ensure that the mounting apparatus can handle the load being applied by the actuator.
Applications of Micro and Mini Actuators

The versatility of micro and mini compact actuators with efficient operations, durable construction, customization options, and high performance specifications opens a world of endless possibilities. Here are a few example applications and industries where they are used in:
- Home automation: The added convenience and safety of having security door locks, motorized louvered roof pergolas, automatic doors, and hidden entrance projects are just a few areas at home that benefit from micro and mini compact actuators. Their space efficiency, low maintenance requirements, and simple operation make them popular in commercial use as well as the DIY community of homeowners.
- Custom/DIY Projects: In many cases, prototyping a new product or creating small-scale versions is a critical step in the process of helping determine potential challenges that may need to be addressed before proceeding with a finalized project. Micro and mini actuators with their compact body and versatile specifications help drive motion to demonstrate a proof of concept as a way to simulate a full-sized project.
- Medical industries: In the medical field, precision control of micro actuators is critical for equipment designed for handling fluid flow, driving surgical robots, or positioning medical equipment. Adjustable beds, chairs, rehabilitation equipment, and imaging equipment may incorporate mini actuators for driving quiet and smooth motion in hospital settings.
- Automotive industries: Use cases include opening storage compartments, raising campers, mirror tilting, window adjustments, and automating roof conversions. Combining the advantages of micro and mini actuators helps enhance a user’s driving and ownership experience without taking up much space thanks to their compact form factor.
- Entertainment Industry: Amusement parks and Halloween costumes utilize animatronics, movie robots, and special effects props that captivate an audience through life-like motion. These are made possible through the wide variety of configurations available in micro and mini actuators to handle demanding space restrictions, force rating requirements, and outdoor environments while being energy efficient.
The Future of Micro and Mini Electric Linear Actuators
While micro and mini electric linear actuators may not gain the most news attention in the tech world, they do play a crucial role in pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As technology advances, the demand for smaller and more efficient components will continue to rise.
Whether you are designing the next revolutionary gadget or developing cutting-edge medical equipment, micro and mini actuators have a promising future ahead and could be the compact solutions you didn’t know you needed.
Material Enhancements
Materials will play a pivotal role in enhancing the performance and durability of actuators. The development of advanced composites will allow for lighter, more resilient actuators that can withstand higher loads and operate in more extreme environments. These materials will also contribute to reducing the overall size of actuators without compromising structural integrity and power output.
Greater Performance
Overall performance of mini and micro actuators is expected to become more refined, with a focus on increasing the force-to-size ratio. This will be achieved through the integration of high-efficiency motors and optimized gear systems, allowing for greater precision and control. Additionally, the miniaturization of components will enable compact actuators to fit into increasingly smaller spaces, broadening their application scope.
Accuracy Improvements
Positional feedback accuracy is expected to see substantial improvements through the incorporation of advanced sensor technologies. The use of optical encoders, Hall effect sensors, and other high-resolution feedback mechanisms in development will provide precise control over actuator movement. This will be crucial in applications where exact positioning is critical, such as in surgical robots or precision manufacturing equipment.
In Summary
Micro and mini actuators are versatile components in optimizing applications with space constraints to their maximum potential thanks to their durability, efficiency, and precision. By understanding the different types of micro and mini actuators, their specifications, and the process of selecting suitable models, users can ensure optimal operation and achieve the results that meet the needs of their application.
We hope you found this as informative and interesting as we did, especially if you were looking for guidance in choosing suitable micro and mini electric linear actuators for your application. If you have any queries about our products or have trouble picking out the right electric linear actuators to suit your needs, feel free to reach out to us! We are experts in what we do and will be happy to help with any questions you may have!
Mini actuators have a larger size than micro actuators, however, mini actuators still have a compact design being approximately half or a third of the dimensional volume of standard type actuators.
Our micro actuators are available in stroke lengths ranging from 0.5 - 12 inch while our mini actuators range from 2 - 40 inch.
The voltage requirements of our actuators vary from model to model, however, the majority of our models have options or come standard with 12 VDC operation.
The IP ratings of our actuators vary from model to model, however, micro and mini actuators can range from IP54 to IP66.
Synchronous motion for multiple actuators is possible when the actuators have built-in positional feedback such as hall effect sensors paired with the compatible hall effect control boxes that have been programmed to keep them in sync.
